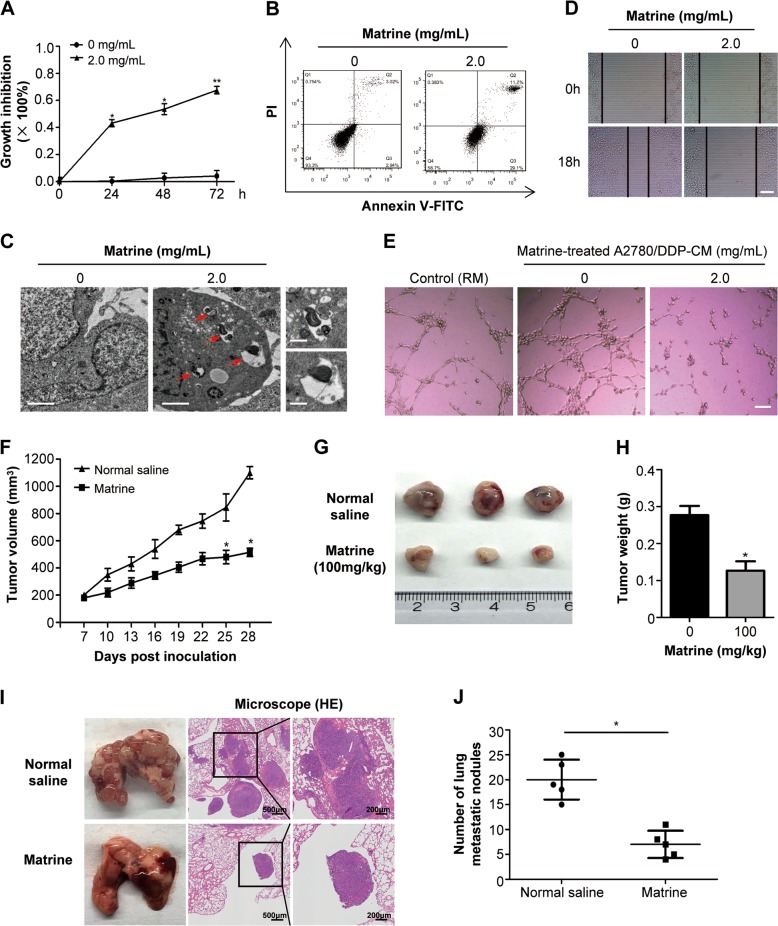
Fig. 7. The antitumor effects of matrine on A2780/DDP in vitro and in vivo.
a The proliferation inhibition of matrine in A2780/DDP cells was determined by MTT assay. Data are presented as mean ± SD from three independent experiments (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01). b Changes in apoptosis in matrine treated A2780/DDP cells were determined by flow cytometry analysis. c Autophagosome and autolysosome vesicles of A2780/DDP cells treated with 2.0 mg/mL matrine for 24 h were visualized by transmission electron microscopy. The typical images of autophagosomes and autolysosomes were indicated at the red arrows (scale bar: 2 μm). On the right panel were images with higher magnifications (scale bar: 0.5 μm). d Wound healing assay was performed to examine the effect of matrine on the migration of A2780/DDP cells. Scale bar: 50 μm. e Matrine inhibited the tube formation of HUVECs in Matrigel in presence of regular media (RM) or A2780/DDP cell derived CM or matrine-treated A2780/DDP cell derived CM. Scale bar: 20 μm. f Effect of matrine on the growth of A2780/DDP xenograft tumors. The changes of tumor volumes were shown between matrine and normal saline group (n = 3, *P < 0.05). g Tumors in matrine-treated mice were significantly smaller than those in normal saline group. h The bar graph represented the mean of tumor weight from matrine-treated and control mice (n = 3, *P < 0.05). i Representative images of lungs with metastatic nodules (left panel) and the corresponding images of H&E-stained lungs with metastases (middle and right panels). j The lung metastatic nodules were examined and quantified in mice treated with matrine and normal saline