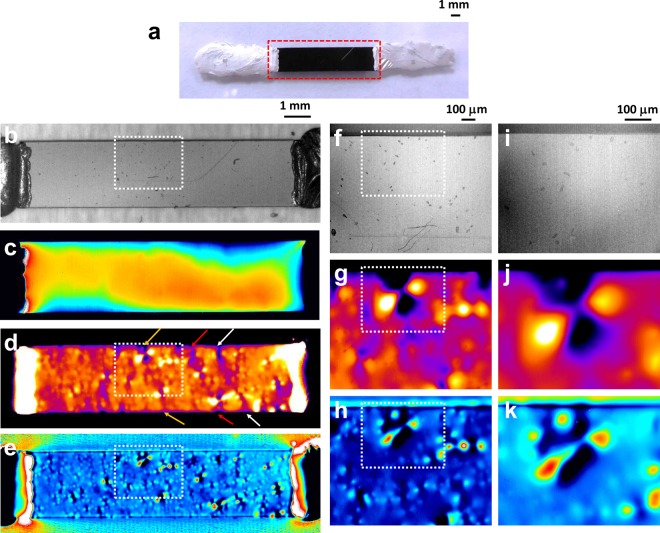
Figure 2.
(a) Optical image of CNT/PC sample. Composite materials containing CNTs have an almost completely black surface, and the conventional optical method is not effective with these kinds of materials. (b–e) from top to bottom, low-magnification infrared, conventional-accumulation, intensity and phase images of the same sample shown in (a). In the infrared image, the sample showed a relatively flat and clean surface except for some particles and scratches. Moreover, the conventional method images showed only some blurred intensity distribution as shown in (c). The intensity (d) and phase (e) images show the heat distributions reflecting the network structures and local resistance. The pairs of arrow indicated in (d) indicate the higher-resistance cross sections across the current flow direction. (f–k) The middle- (f–h) and high- (i–k) magnification images show the pair of hot spots near the high-resistance cross section shown in (d). The narrow conductive channel and voltage concentration are clearly observed in these results. All LIT images were obtained by applying 60-V and 6.4-mA bias conditions and using 10-minute accumulation.