Figure 1.
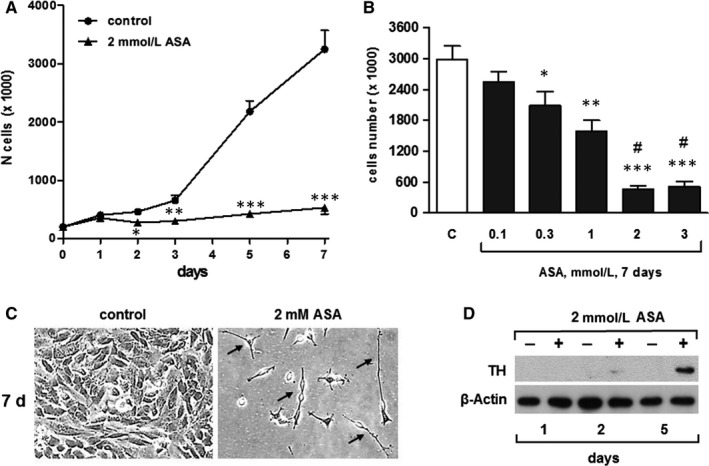
ASA inhibits the proliferation and induces neuronal‐like differentiation of SK‐N‐SH (N) cells in a time‐ and concentration‐dependent manner. A, Time course of the effects of ASA on SK‐N‐SH (N) cells. Cells were incubated with vehicle (control) or with medium containing 2 mmol/L ASA for the indicated times. Results are from three independent experiments performed in duplicate. *P < .05, **P < .01 and ***P < .001 (vs control). B, Concentration dependence of the effects of ASA on SK‐H‐SH (N) cells. Cells were incubated with vehicle or with medium containing increasing concentrations of ASA for 7 d. Results are from three independent experiments performed in duplicate. *P < .05, **P < .01 and ***P < .001 (vs control); #P ˂ 0.05 (vs 0.3 mmol/L ASA). C, Light microscopic representative images at ×200 magnification showing ASA‐treated SK‐N‐SH (N) cells vs control, after 7 d. D, Representative Western blot experiment showing the time course of the effects of ASA on tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) in SK‐N‐SH (N) cells
