Figure 3.
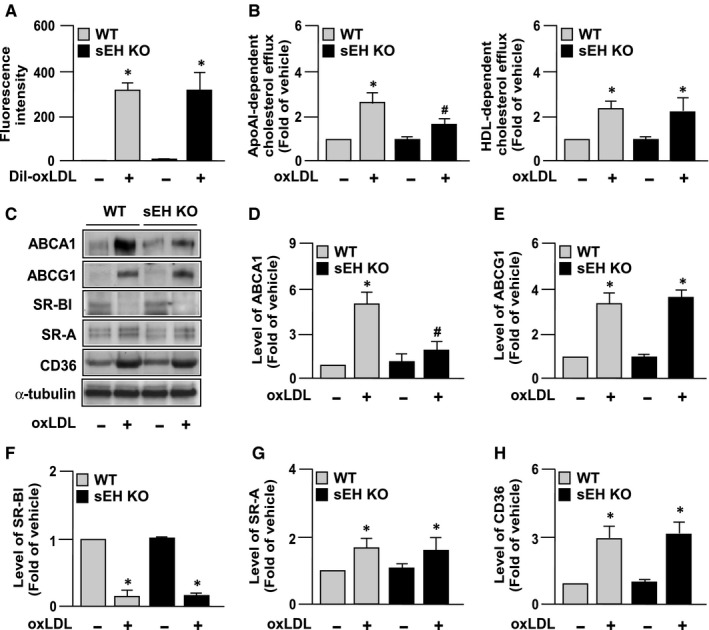
Genetic deletion of sEH impairs cholesterol efflux and down‐regulates expression of ATP‐binding cassette transporter A1 following oxLDL treatment in macrophages. A, For Dil‐oxLDL binding assays, WT or EPXH2 −/− sEH‐deficient (sEH KO) macrophages were treated with or without Dil‐oxLDL (10 µg/mL) for 4 h at 4°C. Cellular lysates were analysed by fluorometry. B, Macrophages were treated with NBD cholesterol (1 µg/mL) for 12 h, followed by oxLDL (50 µg/mL) in the presence of apoAI (10 µg/mL) or HDL (50 µg/mL) for an additional 12 h. Cholesterol efflux was quantified as a percentage of fluorescence in the medium relative to the total amount of fluorescence. C‐H, BMDMs were incubated with 50 µg/mL oxLDL for 24 h and cell lysates were subjected to (C) Western blotting. Blots were quantitated to determine the protein levels of (D) ABCA1, (E) ABCG1, (F) SR‐BI, (G) SR‐A, (H) CD36, with α‐tubulin as a control for normalization. Fold induction was defined as level of protein relative to the untreated group set as 1. Data shown are mean ± SD from 5 independent experiments. *P < 0.05 vs untreated groups, #; P < 0.05 vs oxLDL‐treated WT macrophages
