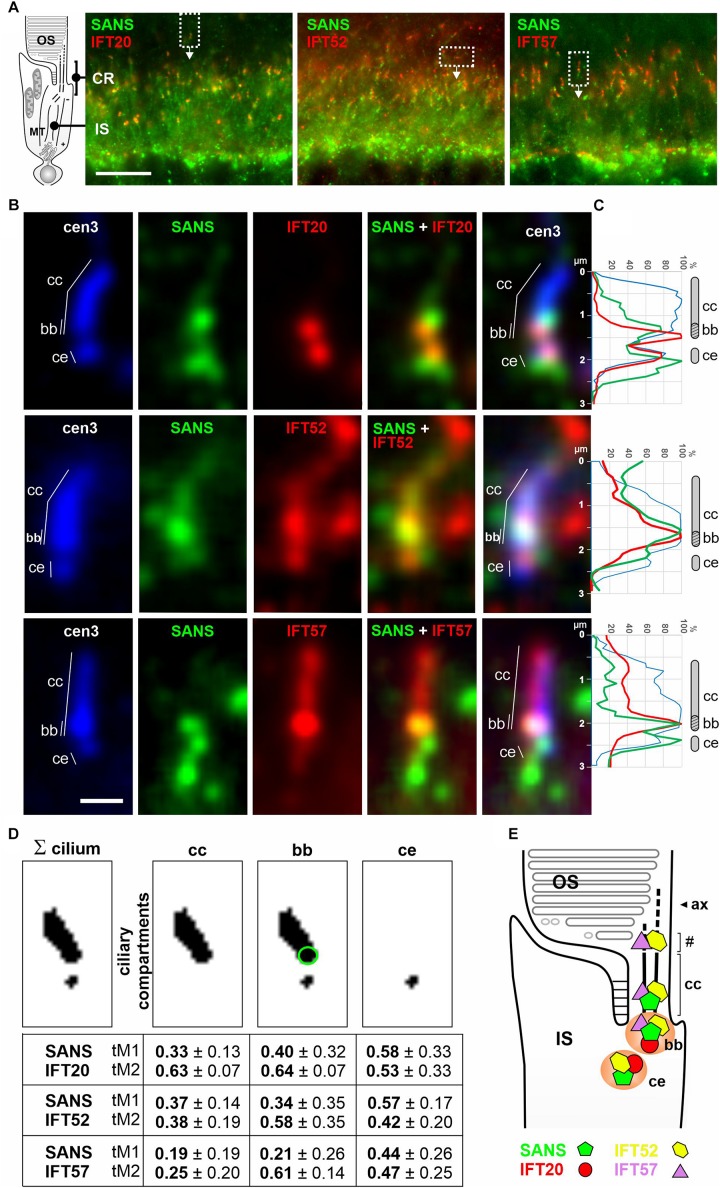
FIGURE 4.
Subcellular localization of SANS and IFT-B proteins in the ciliary region of murine photoreceptor cells. (A) Indirect immunofluorescence triple labeling of SANS and with IFT20, IFT52, and IFT57 of photoreceptor layers in longitudinal cryosections of murine wild type retinas co-stained with anti-centrin3 (cen3), a marker for the connecting cilium (cc), basal body (bb) (mother centriole), and the adjacent (daughter) centriole (ce) of photoreceptor cells. CR, ciliary region; OS, photosensitive outer segments; the IS, inner segment; MT, microtubule tracks through the IS. (B) High magnification of photoreceptor cilia from areas indicated by rectangles in (A). (C) Intensity plots of the immunofluorescence of the photoreceptor cilia shown in (B). (D) Measurements of the Manders’ Colocalization Coefficients (MCC) of subciliary compartments of photoreceptor cilia, namely the cc (highlighted by green circle) and ce. Numbers from 0 to 1 indicate increasing co-localization of molecules M1 (SANS) and M2 (IFT). (E) Schematic illustration of the localization of SANS (green), IFT20 (red), IFT52 (yellow), and IFT57 (purple) in photoreceptor cilia. Partial co-localization of SANS with the IFT-B molecules at the ciliary base is indicated by orange color. # indicates OS base where disk neogenesis takes place. Ax, axoneme. Scale bar: 10 μm (A); 1 μm (B).