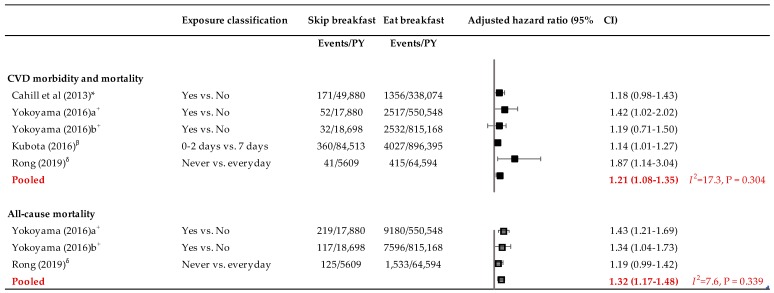
Figure 2.
Forest plot of the association between breakfast skipping and cardiovascular disease morbidity and mortality and all-cause death. Covariates adjusted for in individual studies: * In addition to age, diet, demographic, and activity factors, this model was further adjusted for the body mass index (BMI) updated every 2 years (<18.5, 18.5–24.9, 25–29.9, ≥30 kg/m2, missing) as well as diabetes mellitus (yes/no), hypertension (yes/no), and hypercholesterolemia (yes/no), also updated every 2 years. + Adjusted for age and history of hypertension, history of diabetes mellitus, body mass index, smoking status, alcohol status, education level, physical activity, walking duration, sleep duration, marital status, and work schedule. β Adjusted for age, sex, ethanol, energy, and intake of vegetables, fruits, fish, soy, milk/dairy products, nuts, saturated fatty acid, dietary fiber, and sodium, as well as smoking status, leisure-time sports, sleep duration, perceived mental stress, living alone, physical labor, and public health center area. δ All models were adjusted for age, sex, race/ethnicity, marital status, family income level, smoking status, alcohol intake, physical activity, total energy intake, overall diet quality indicated by the Healthy Eating Index—2010, body mass index, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and dyslipidemia. CI = confidence interval.