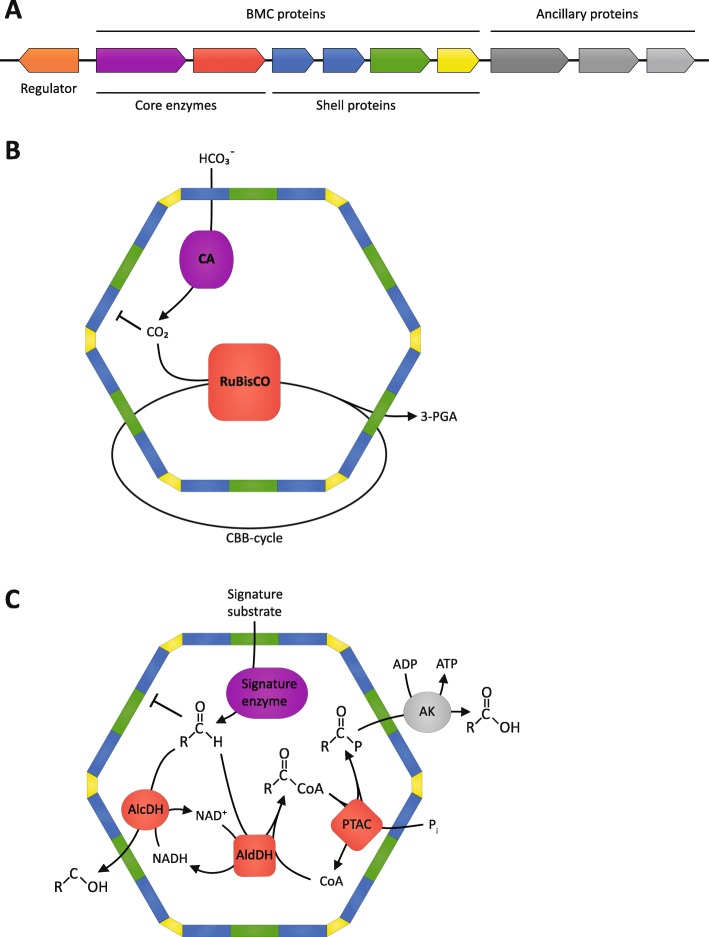
Fig. 2.
BMC genetic and metabolic modularity. a Schematic of a BMC gene locus containing a transcriptional regulator (orange) presumably controlling the expression of the BMC operon, the enzymatic core (purple and red), the structural shell proteins (blue, green, and yellow) forming the BMC and the ancillary proteins positioning and metabolically integrating the BMC into the cell (gray). b Schematic function of the carboxysome. The shell acts as a barrier to concentrate the CO2 and potentially exclude the competitive inhibitor oxygen within the BMC, enabling RuBisCO to operate more efficiently. 3-PGA 3-phosphoglycerate. c Schematic function of metabolosomes. The toxic aldehyde intermediate is contained and detoxified within the BMC. CoA coenzyme A, Pi inorganic phosphate