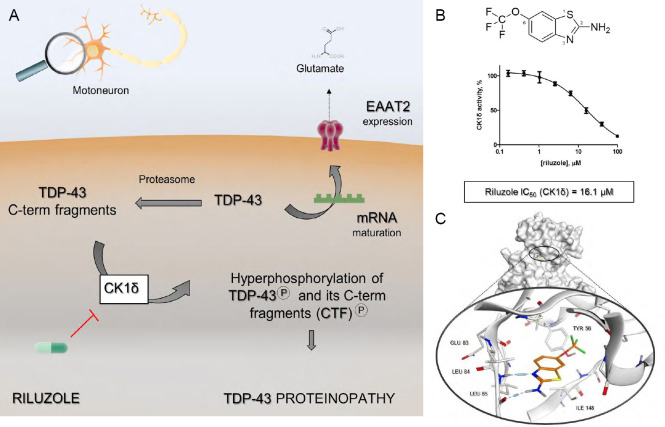
Figure 1.
Unmasking the molecular link between riluzole and protein kinase CK1δ.
(A) Riluzole revisited mechanism of action: the aberrant phosphorylation of the full-length nuclear protein TDP-43 and its C-term fragments (CTF) generated by proteasome complex, is modulated through the inhibition of CK1δ catalytic activity. As a result, riluzole prevents the cascade of events that culminates with TDP-43 compartmentalization at the cytoplasmic level. The maintenance of TDP-43 homeostasis assured by riluzole allows the correct maturation of specific mRNA transcripts and therefore the normal expression of the EATA2 transporter, which prevents the lethal phenomenon of excitotoxicity. (B) the chemical structure of 1,6-(trifluoromethoxy)-2-benzothiazolamine, commonly known as riluzole. The IC50 value for protein kinase CK1δ inhibition, quantify through a biochemical assay, has been reported, to underline the link between CK1δ and ALS treatment. (C) The proposed binding mode of drug riluzole inside CK1δ catalytic site, predicted through molecular docking experiments. ALS: Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; CK1δ: protein kinase CK1 isoform δ; TDP-43: transactive response DNA binding protein of 43 kDa; EAAT2: excitatory amino acid transporter-2.