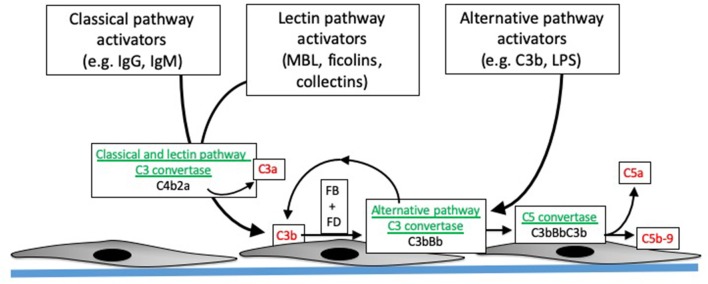
Figure 1.
Overview of complement activation. Specific activating molecules engage the classical, lectin, and alternative pathways. Cleavage of C4 and C2 generates C4b2a, the classical and lectin pathway C3 convertases (enzymes that cleave C3). C3 generated by the classical and lectin pathways can combine with factor B (FB), which is then cleaved by factor D (FD), to form C3bBb. C3bBb is the alternative pathway C3 convertase, and can also be generated by spontaneous formation of C3b. The C3 convertases combine with another C3b to form the C5 convertase, which then cleaves C5 into C5b and C5a. C5b combines with C6, C7, C8, and C9 to form C5b-9, or the membrane attack complex. The convertases are depicted in green, and pro-inflammatory molecules generated during complement activation are shown in red.