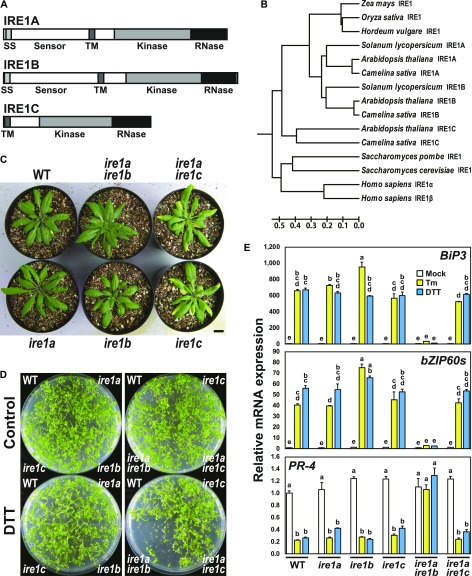
Figure 1. Arabidopsis IRE1C does not contribute to the UPR.
(A) Structures of Arabidopsis IRE1A, IRE1B, and IRE1C proteins. (B) Phylogenetic tree of IRE1 proteins from mammals (Homo sapiens), fungi (Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Saccharomyces pombe) and plants was constructed by UPGMA using MEGA 6 (Tamura et al, 2013). The tree is drawn to scale, with branch lengths in the same units as those of the evolutionary distances used to infer the phylogenetic tree. The evolutionary distances were computed using the Poisson correction method and are in the units of the number of amino acid substitutions per site. (C) Wild-type (WT) and ire1 mutant plants 40 d after germination (DAG). Bar = 10 mm. (D) DTT sensitivity of the ire1 mutants. Seedlings at 15 DAG of the indicated lines were treated with or without 1 mM DTT. (E) The relative mRNA levels of BiP3 (upper), bZIP60s (middle), and PR-4 (lower) in WT and ire1 mutants. RNA from seedlings at 10 DAG were treated with 5 mg/l Tm, 2 mM DTT, or mock for 5 h and subjected to qPCR. Data are means ± SEM of three independent experiments. Different letters within each treatment indicate significant differences (P < 0.05) by the Tukey–Kramer Honestly Significant Difference (HSD) test. SS, signal sequence; TM, transmembrane domain.