Figure 4. Computational prediction of antibiotic resistance.
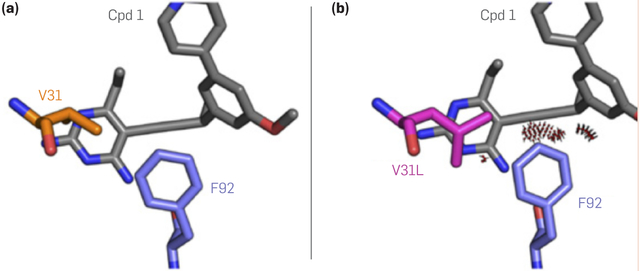
(a) the bacterial (Staphyoloccus aureus) enzyme dihydrofolate reductase binds a drug candidate (“Cpd 1”) tightly, inhibiting the enzyme’s function, but (b) mutating position 31 of the enzyme from amino-acid type valine to leucine causes steric clashes that impeded binding, allowing the bacteria to resist the antibiotic. This predicted resistance mutation was observed experimentally after being predicted by the K* algorithm as implemented in the OSPREY software.19 Figure adapted with permission from Reeve et al.28
