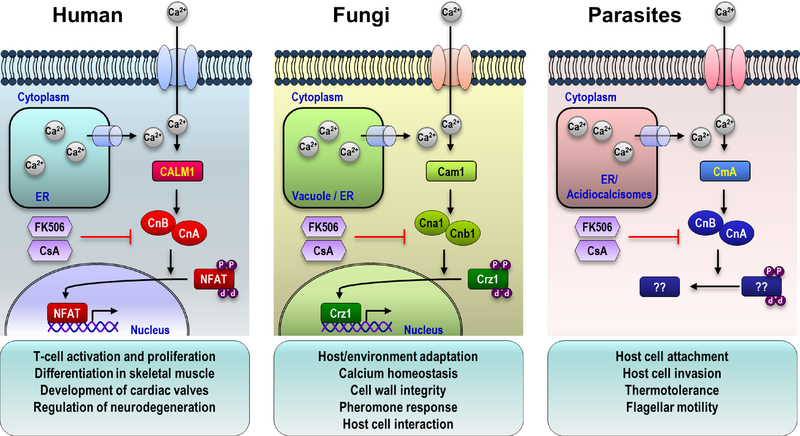
Figure 1. The calcineurin signaling pathway in mammals, fungi, and protists.
In response to external or internal signals, intracellular calcium concentrations increase via uptake from the extracellular milieu or by release from intracellular stores. Calcium ions bind to the calcium binding protein calmodulin, which in turn binds to and stimulates calcineurin protein phosphatase activity. Activated calcineurin dephosphorylates target proteins, including NFAT and Crz1, enabling appropriate cellular responses.