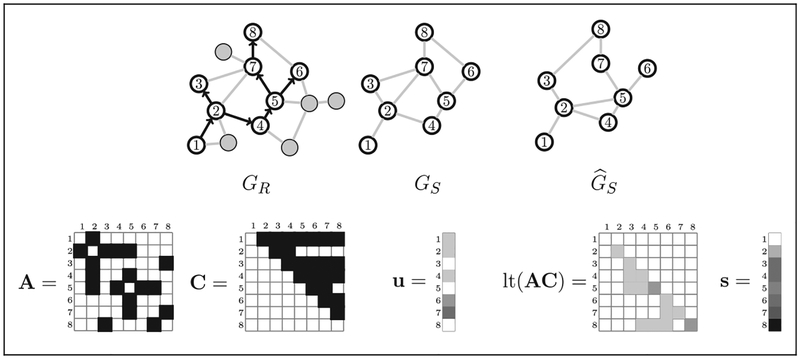
Figure 2.
Examples of matrices used to calculate the recruitment time series likelihood. At top left is the recruitment graph GR overlaid on the population graph G, with recruited vertices numbered and other vertices and edges in gray. The true recruitment-induced subgraph GS is not directly observed. We estimate GS by and let A be the adjacency matrix of . The coupon matrix C and the number of pendant edges attached to each recruited vertex is u. Pendant edges connect recruited vertices to unknown/unsampled vertices. The i, jth element of lt(AC) is the number of recruiters connected to i just before the jth recruitment event.