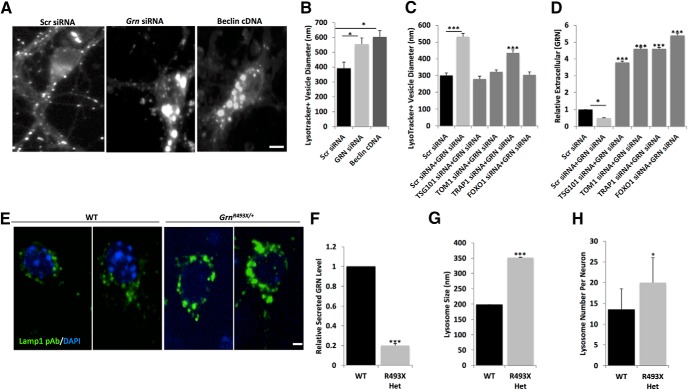
Figure 8.
Reduced progranulin levels lead to enlarged lysosomes in mouse cortical neurons. A, Images of mouse WT primary cortical neurons cotransfected with pGW1EGFP and Scr siRNA, Grn siRNA, or Beclin cDNA and stained with Lysotracker red. Scale bar, 10 μm. B, Diameters of Lysotracker red-positive structures measured in ImageJ. C, Diameters of Lysotracker red-positive structures measured in ImageJ for mouse cortical neurons transfected with Scr siRNA alone, Scr siRNA + Grn siRNA, Tsg101 siRNA + Grn siRNA, Tom1 siRNA+ Grn siRNA, Trap1/Hsp90L siRNA+ Grn siRNA, or Foxo1 siRNA+ Grn siRNA. D, Extracellular progranulin levels measured by ELISA in mouse cortical neurons transfected with Scr siRNA alone, Scr siRNA + Grn siRNA, Tsg101 siRNA + Grn siRNA, Tom1 siRNA+ Grn siRNA, Trap1/Hsp90L siRNA+ Grn siRNA, or Foxo1 siRNA+ Grn siRNA. Statistical test: Student's t test, *p < 0.05; ***p < 0.001. E, Representative images of LAMP1+ (green) lysosomes in control littermate WT neurons (left two panels) or in Grn-deficient (Grn493X/+) neurons (right two panels) also stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 5 μm. Grn-deficient (Grn493X/+) neurons have reduced progranulin levels (F), increased lysosome size (G), and increased lysosome numbers (H). Statistical test: Student's t test, ***p < 0.001.