Figure 2.
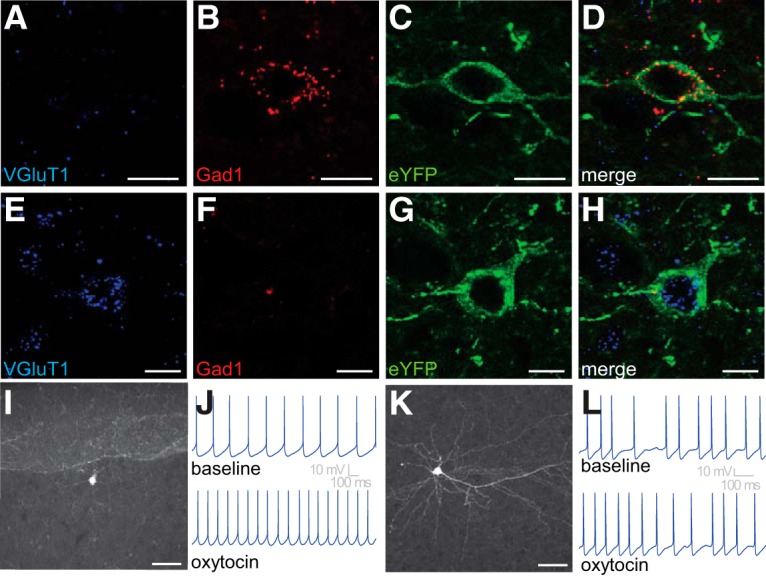
Neurochemical and electrophysiological phenotypes of OXTR-expressing neurons in the PFC. A–H, Representative images of PFC neurons labeled for VGlut1 mRNA (blue) or Gad1 mRNA (red) and eYFP (green). A, VGlut1 mRNA is scant, but (B) Gad1 mRNA is abundant and (C,D) colocalizes with eYFP, indicating that some OXTR-expressing neurons in the PFC are GABAergic. In a different cell within the PFC, (E) VGlut1 mRNA is abundant, but (F) Gad1 mRNA is scant and (G,H) VGlut1 mRNA colocalizes with eYFP, indicating that some OXTR-expressing neurons in the PFC are glutamatergic. I, J, Interneuron-like eYFP-labeled neurons in the PFC are excited by bath application of 200 nm oxytocin (example recorded under constant 50 pA current injection). K, L, Pyramidal-like eYFP-labeled neurons in the PFC are also excited by bath application of 200 nm oxytocin (example recorded under constant 300 pA current injection). Scale bars: A–H, 10 μm; I, K, 50 μm.
