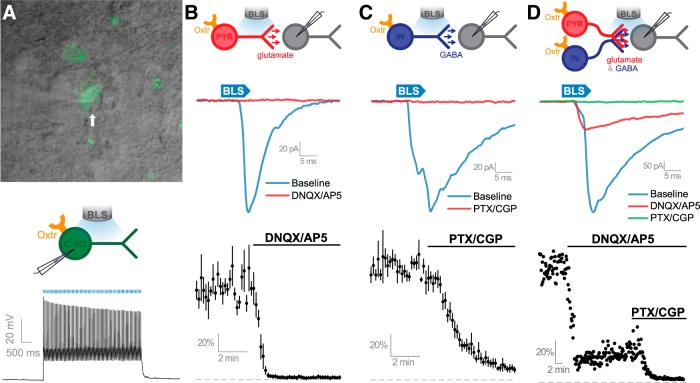
Figure 3.
OXTR-expressing neurons release glutamate and GABA onto neighboring neurons in the PFC. A, Top, Viral delivery of eYFP and ChR2 into OXTR-expressing neurons allows their identification with epifluorescence and DIC microscopy. Middle, Schematic of patch-clamp recordings obtained from OXTR-expressing neurons transfected with ChR2 that were exposed to blue light stimulation (BLS). Bottom, A pulse train of BLS reliably causes the generation of action potentials in OXTR-expressing neurons in the PFC that were transfected with ChR2 (BLS, 20 ms pulses, 15 Hz). B, Top, Schematic of patch-clamp recordings taken from PFC postsynaptic neurons identified as receiving synaptic inputs from eYPF/ChR2-positive OXTR-expressing glutamatergic neurons in the PFC. Middle, In some eYFP/ChR2-negative PFC pyramidal-like neurons, BLS evoked synaptic currents (blue trace) that are blocked by bath application of ionotropic glutamate receptor antagonists (red trace). Bottom, Average normalized response to BLS from all cells studied that had evoked responses sensitive to glutamate receptor antagonists DNQX and AP5. C, Top, Schematic of patch-clamp recordings taken from PFC postsynaptic neurons identified as receiving GABAergic inputs by BLS of OXTR-expressing neurons. Middle, BLS evokes synaptic currents in conditions that isolate GABAergic signaling. Bottom, Average normalized light-evoked GABA current of all cells studied demonstrating sensitivity to GABA receptor antagonists PTX and CGP. Scale bar: A, 20 μm. D, Top, Schematic depicting that OXTRs are expressed by pyramidal or interneurons with BLS eliciting glutamate and GABA release onto the same postsynaptic neuron. Middle, Representative responses to BLS. Bottom, Normalized light-evoked response was partially DNQX/AP5 sensitive and fully eliminated by PTX/CGP.