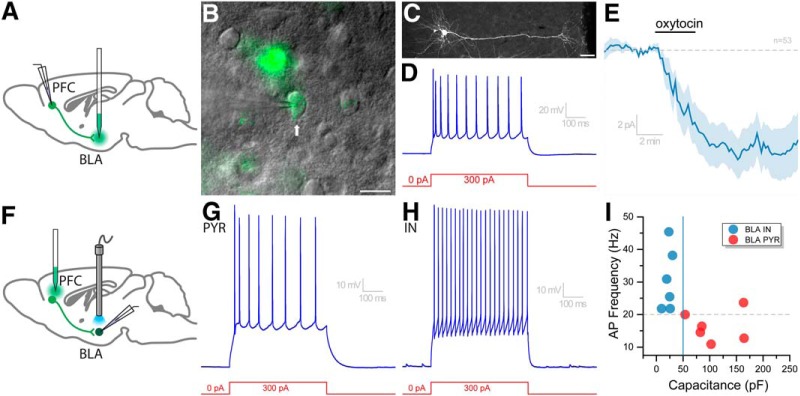
Figure 8.
Oxytocin depolarizes BLA-projecting PFC neurons that release glutamate onto pyramidal (PYR) and interneurons (IN) in the BLA. A, Retro-fluorescent microspheres were injected into the BLA of WT mice to identify and obtain electrophysiological recordings from neurons in the PFC with direct projections to the BLA. B, Using epifluorescence with DIC microscopy, retrogradely labeled (green) PFC neurons were targeted for patch-clamp analysis. These neurons had (C) morphology and (D) firing properties like those of pyramidal neurons in Figure 2K–L. E, Average response of all retrogradely labeled cells to oxytocin (3 min, 200–400 nm; n = 53). F, Injection of Cre-inducible AAV-ChR2-eYFP into the PFC of Oxtr-Cre mice allows for CRACM in the BLA. G–I, BLS induced EPSCs in both small and large BLA neurons that exhibited a wide range of firing frequencies in response to a 300 pA current injection. Among the light responsive BLA neurons, large capacitance slow firing cells were considered likely to by pyramidal neurons, whereas small capacitance faster firing cells were considered likely to be interneurons. Scale bars: B, 20 μm; C, 50 μm.