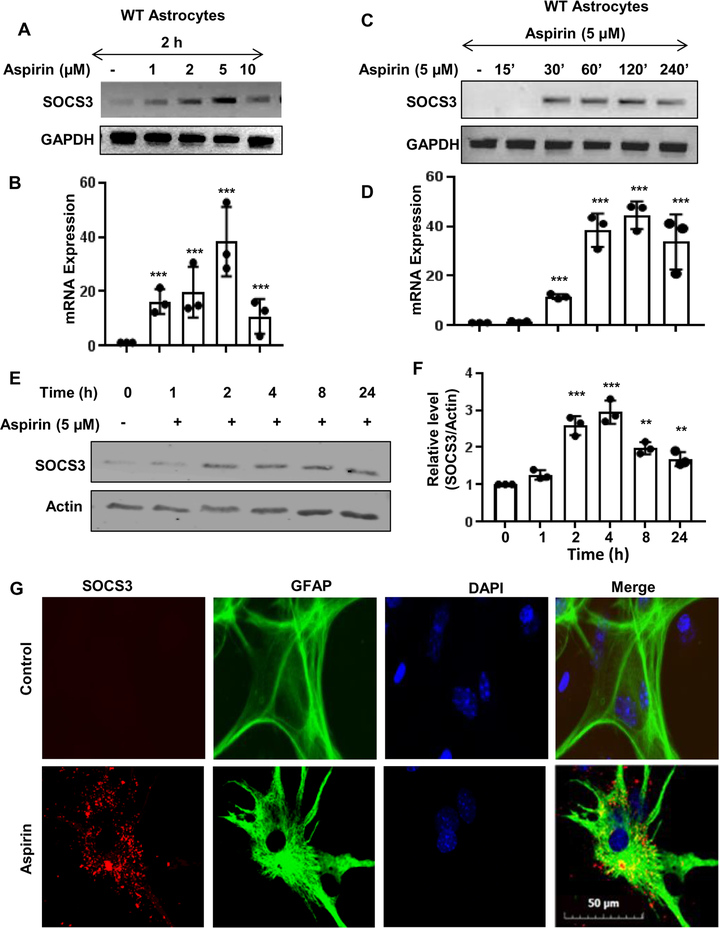
Figure 1. Aspirin upregulates SOCS3 mRNA and protein in primary mouse astrocytes.
Astrocytes were treated with different concentrations of aspirin for 2 h under serum-free condition followed by monitoring the mRNA expression of Socs3 by semi-quantitative RT-PCR (A) and real-time PCR (B). One-way ANOVA was adopted to test the significance of mean between groups with dose as a single factor. The resultant statistics is F4, 10 =8.8235 (>Fc =3.47); p<0.005 (=0.002). A paired t-test to analyze the significance of mean between two groups provides ***p= 0.004675(<0.005) and 0.00315 (<0.005) when comparing control with aspirin 1 and 2 μM, respectively. Moreover, 5 μM aspirin showed higher statistical significance with respect to control as evident from p =0.000073 (<0.001). A paired t-test analysis to compare between 2 and 5 μM aspirin showed strong significance with p=0.0135 (<0.05). Cells were treated with 5 μM aspirin under serum-free condition for different time points followed by monitoring the mRNA expression of Socs3 by semi-quantitative RT-PCR (C) and real-time PCR (D). Similarly, ANOVA with time as a single factor results F6, 11 =25.5 (>Fc =3.09); p<0.001(=7.6 *10−6). ***p= 0.0028 (<0.05) when compared control with aspirin 30 min. The protein expression of SOCS3 was examined by Western blot (E). Actin was run as a loading control. Bands were scanned and values (SOCS3/Actin) presented as relative to control (F). A two-tailed paired t-test was performed to test the significance of mean between control and aspirin-treated groups. Results are mean ± SD of three independent cell preparations. **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001 vs control. Cells were treated with 5 μM aspirin under serum-free condition for 4 h followed by double-label immunofluorescence for GFAP and SOCS3 (G). Results represent three independent cell preparations.