Fig. 3.
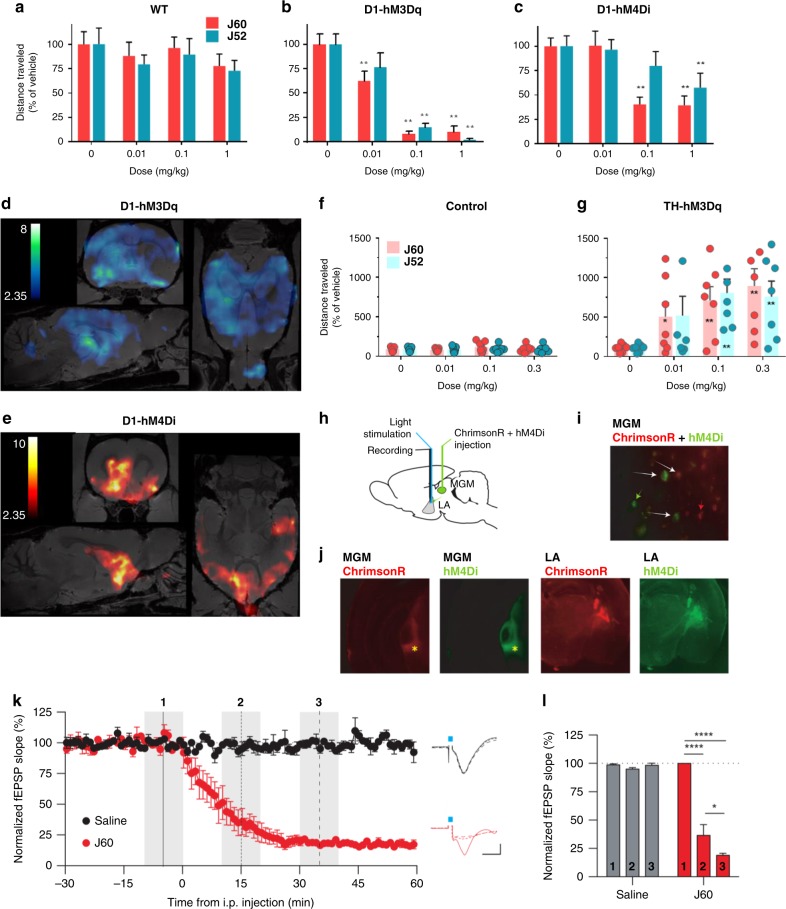
JHU37152 and JHU37160 exhibit high in vivo DREADD potency. a–c J60 and J52 produce potent inhibition of locomotor activity in transgenic D1-DREADD mice but not in wild-type (WT) mice (n = 7 to 19 mice per condition). Two-way repeated measures ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparison tests were performed, *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 compared with the respective vehicle. d, e DREADD-assisted metabolic mapping (DREAMM) using [18F]FDG in D1-hM3Dq and D1-hM4Di mice (n = 4 mice per condition) reveals opposing and differential recruitment of whole-brain functional networks. f, g J52 and J60 produce potent activation of locomotor activity in rats (n = 7 rats per condition) expressing hM3Dq in tyrosine hydroxylase (TH)-expressing neurons in the ventral tegmental area. One-way repeated measures ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparison tests were performed, *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 compared with the respective vehicle. h–j Design of in vivo electrophysiological experiment and IHC showing hM4Di (green) and ChrimsonR (red) expression in the medial division of the medial geniculate nucleus (MGM) and lateral amygdala (LA). k, l J60 (0.1 mg kg−1) produces rapid and potent hM4Di-driven inhibition of light-evoked neuronal activation. Data are represented as mean ± SEM, *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001. Source data are provided as a Source Data file