Fig. 2.
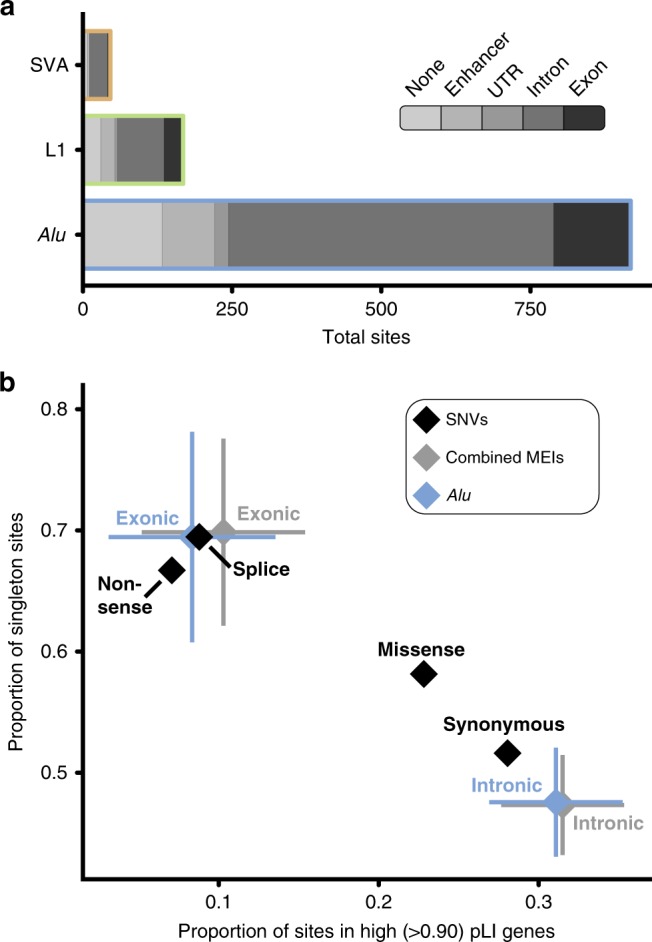
Coding constraint on MEIs. a Cumulative consequence annotations for Alu, L1, and SVA MEIs in all samples (n = 28,132 individuals) analyzed. The majority of variants identified in this study fell within the noncoding space (either an enhancer or intron). b Comparison of constraint between MEIs and SNVs in unaffected parents. To compare the impact of exonic and intronic Alu (blue) and all MEIs (grey) to varying classes of SNVs (black), we used two metrics: the proportion of variants in genes that have been identified as LoF intolerant as gauged by pLI-score22 (x-axis) and the proportion of variants identified in only one individual (i.e., singletons; y-axis). Error bars indicate 95% confidence intervals based on population proportion; confidence intervals were calculated for SNVs, but are too small to appear at the resolution displayed in this figure
