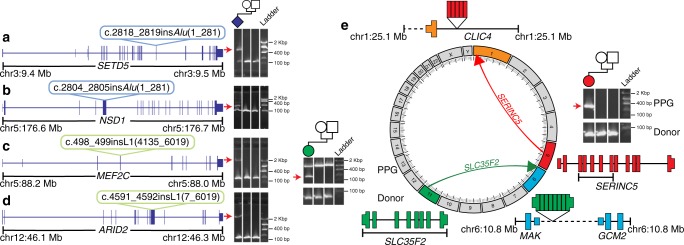
Fig. 3.
RT-derived de novos in the DDD. We identified a total of nine de novo MEIs, four of which disrupted the protein-coding sequence of a known DD gene: a SETD5, b NSD1, c MEF2C, and d ARID2. Shown in each panel is a diagram of the affected gene (blue model) with the relevant insertion indicated with a colored bubble. To the right are PCR validations confirming the de novo status of each mutation; a positive result is indicated by a raised secondary band present only in the proband sample (red arrow). e Circos diagram and PCR results for two identified germ-line de novo PPGs. For each de novo PPG shown is a diagram of the donor gene (gene model), location of duplication as PPG (directional arrow), and new insertion site. Exons from the donor gene included in the PPG are indicated by brackets underneath the donor gene model. To confirm PPG presence, PCR was performed (Methods) on proband, paternal, and maternal gDNA (sample in each lane is shown by pedigree). The band which represents the PPG is marked with a red arrow, and was confirmed via capillary sequencing (Supplementary Fig. 12). Dashed lines indicate intergenic regions, all genes models are shown in sense orientation, and PPG gene diagrams are not to scale