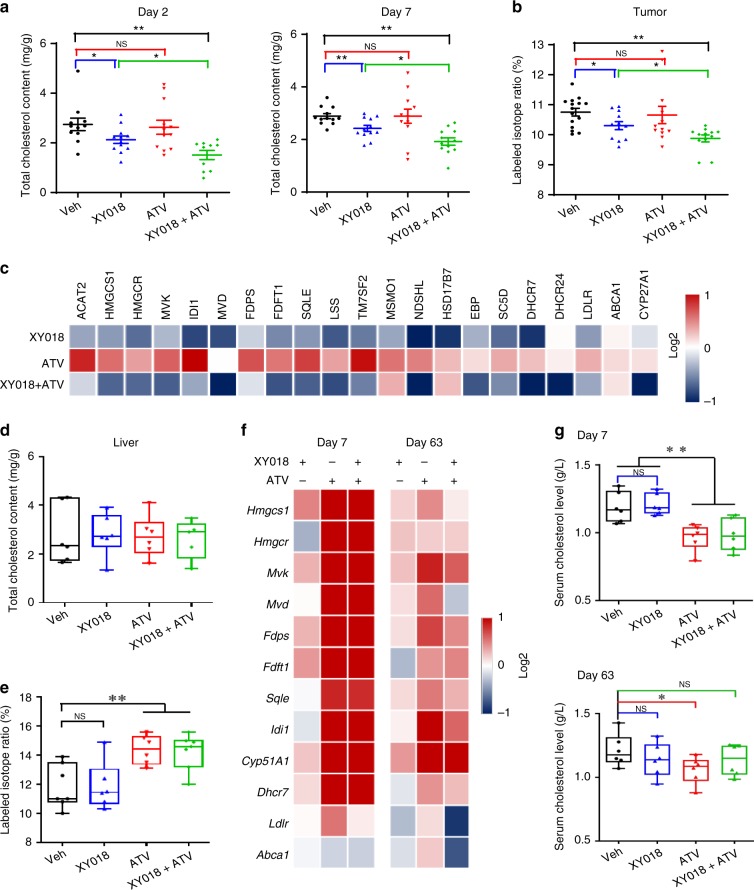
Fig. 7.
RORγ inhibitor reduces TNBC tumor cholesterol biosynthesis in vivo. a Total tumor cholesterol content from HCC70 tumor-bearing mice with indicated treatments for 2 or 7 days was analyzed after organic extraction. n = 12–14 tumors per group. b Labeled isotope ratio indicating tumor cholesterol biosynthesis rate was measured with GC–MS quantifying deuterated hydrogen incorporation into the newly synthesized cholesterol molecules. HCC70 tumor-carrying mice were treated with XY018, ATV, or both as indicated, then dosed with deuterium oxide for 2 h before tissues were collected. n = 7 mice per group. c Heat map display of fold changes (in log2) of cholesterol-biosynthesis pathway gene mRNA analyzed by qRT-PCR in tumors from HCC70 tumor-bearing mice with indicated treatments for 7 days. n = 7, the experiments were repeated three times. d Total liver cholesterol content from mice in (a) with indicated treatments for 7 days. n = 7. e Labeled isotope ratio of liver cholesterol biosynthesis rate in the mice as in (b). n = 7. f Heat map display of fold changes (in log2) of cholesterol-biosynthesis pathway gene mRNA analyzed by qRT-PCR in livers from TNBC tumor-bearing mice with indicated treatments for 7 or 63 days. n = 7, the experiments were repeated three times. g Total cholesterol levels in serum from mice as in (f) were measured. From a to g, 20 mg/kg XY018 or 15 mg/kg ATV were used. Data are shown as mean ± s.e.m. Student’s t test. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, NS not significant