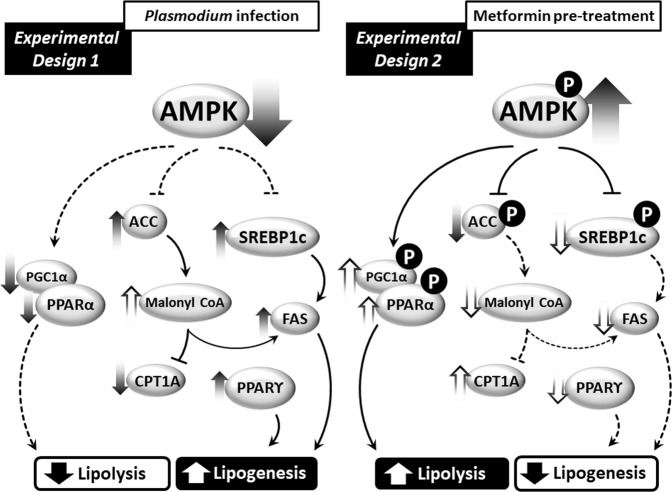
Figure 9.
A working model for the role of the enzyme AMPK in regulating lipid metabolism during P. chabaudi infection. P. chabaudi infection induces a decrease in active hepatic AMPK, which leads to the activation of ACC and SREBP-1c and subsequent stimulation of gene transcription and expression of proteins involved in lipid biosynthesis, such as the enzyme FAS. Concomitantly, there is a reduction of β-oxidation due to the inhibition of the β-oxidation-limiting enzyme CPT1-A and decreased expression of PPAR-α and PGC-1α. Pretreatment with metformin elicits the activation of hepatic AMPK, reversing the lipid metabolism perturbations observed following Plasmodium infection and preventing the efficiency of Plasmodium infection of mice.