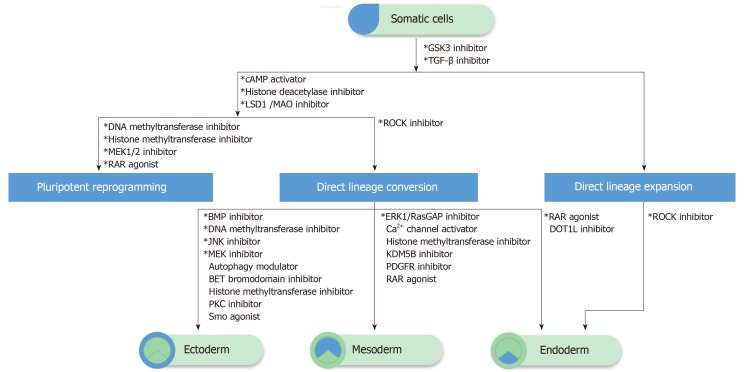
Figure 1.
The schematic of chemical-driven cell fate change and expansion. The transforming growth factor (TGF)-β and GSK3 pathway inhibitors are commonly required in pluripotency reprogramming, direct lineage conversion, and expansion. Additional epigenetic modulators (histone deacetylase inhibitors and/or deoxyribonucleic acid/histone methyltransferase inhibitors) are applied for pluripotency reprogramming, as well as direct lineage conversion, while different lineage commitments require specific signaling modulations. The combination of TGF-β, GSK3, and ROCK pathway inhibitors could induce the direct lineage expansion of endoderm-committed cells such as hepatocytes. The direct expansion of ectoderm and mesoderm-committed cells remains unclear and could not be listed here. *Necessary and/or commonly used compounds.