Figure 1.
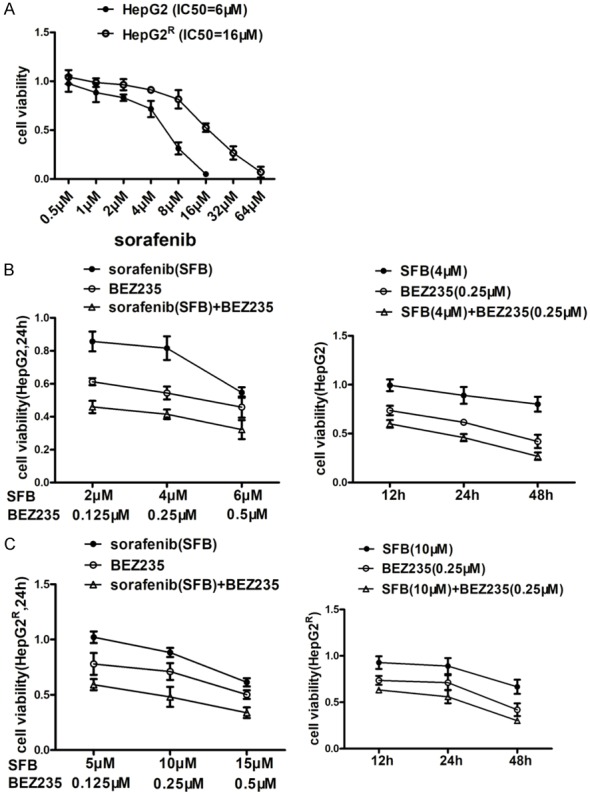
Cell viability of HepG2 and HepG2R cells incubated with sorafenib (SFB), BEZ235, or a combination of sorafenib and BEZ235, measured with MTT assay. A. HepG2 and HepG2R cells were treated with various concentrations of drugs for 24 h and IC50 was calculated as described by Chou et al by MTT assay. The IC50 of sorafenib on HepG2 and HepG2R cells was 6 μM and 16 μM, respectively. B. Left: In comparison with sorafenib, BEZ235 monotherapy and two drugs in combination had a greater effect in reducing the cell viability after 24 h. Also, there was a dose-dependent decrease of cell viability of HepG2 cells treated with sorafenib, BEZ235 or the combination of sorafenib and BEZ235 for 24 h. Right: In comparison with sorafenib (4 μM), BEZ235 (0.25 μM), or combination of sorafenib and BEZ235 decreased cell viability of HepG2 cells for 12 h, 24 h and 48 h. C. The viability of HepG2R cells treated with sorafenib, BEZ235 or in combination was like that of HepG2 cells. Thus, BEZ235 increases sorafenib inhibition of both HepG2 and HepG2R cell viability in a dose- and time-dependent fashion. Compared with control and single-drug treatment, the two drugs in combination were significantly (P<0.05). Data shown are the mean ± SD from three independent experiments.
