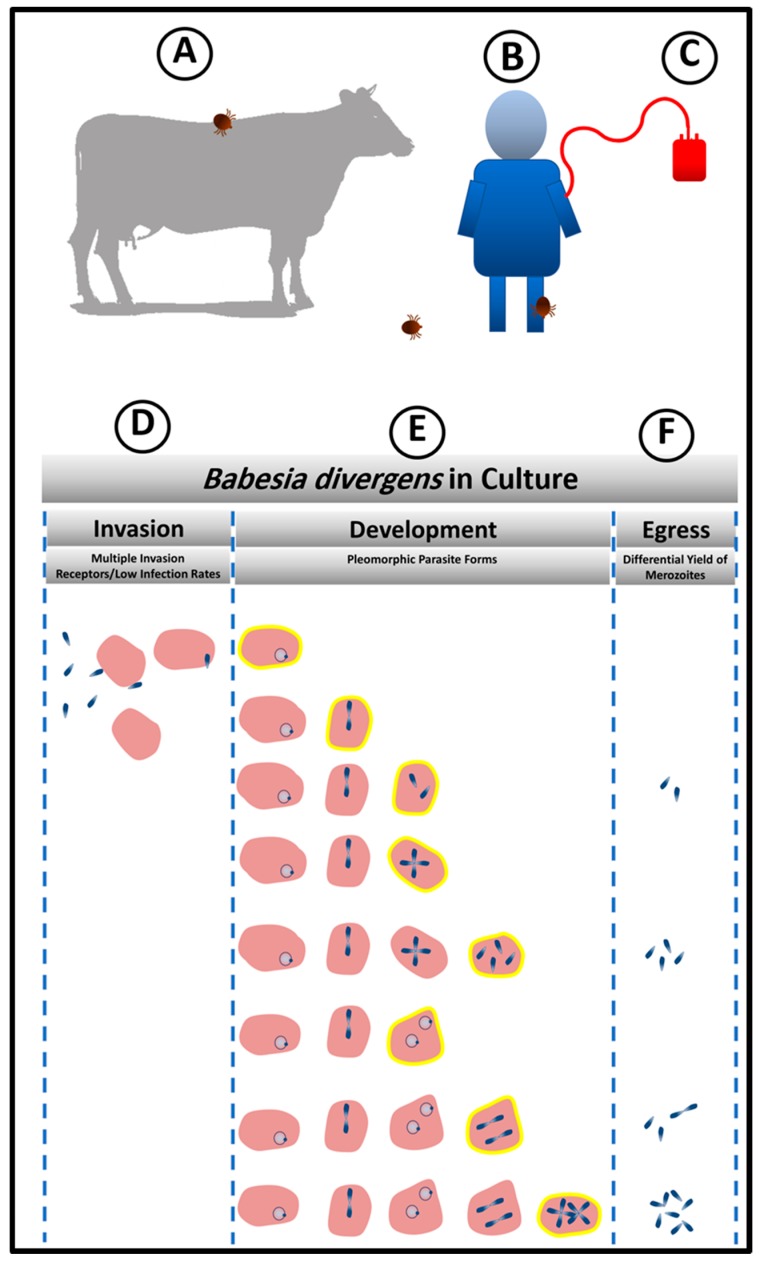
Figure 1.
Persistence Model based on in vitro system. (A,B) Animals and humans get infected by the bites of infected ticks. (C) Babesiosis is also transmitted by blood transfusion. The storage of blood bags at low temperature reduces the size of Bd population. However, once under optimal condition of in vitro culture, Bd is capable of rebuilding its population from few parasites. (D,F) Biological processes that the parasite can control to promote persistence. (D) Control of invasion (E) From the top to the bottom, a complex population structure is built to gain heterogeneity which guarantee the provision of both the number of parasites and parasite stages, for prompt parasite response to environmental changes. Infected RBCs highlighted in yellow represent the diversity of stages and different parasite loads that can stay as the previous stage or keep proliferating within the same host cell to increase the reservoir of infecting individuals. (F) Parasite persistence is controlled by choice of host cells to be lysed and the number of parasites released during egress.