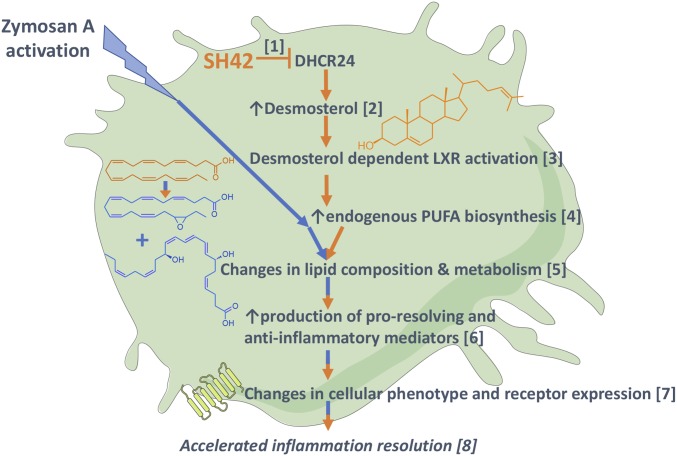
Fig. 10.
Overview and summary of the observed actions of SH42 in a schematic cell. The effects of SH42 are shown in orange, zyA activation is shown in blue, and combined effects are shown in orange/blue. SH42 selectively blocks DHCR24 [1]. Inhibition of DHCR24 leads to increased levels of desmosterol [2]. Desmosterol activates LXRs [3]. LXR activation leads to increased endogenous PUFA biosynthesis [4]. LXR activation leads to changes in lipid composition and metabolism [5]. The altered lipidome results in increased production of antiinflammatory and proresolving LMs after zyA stimulation [6]. LMs are known effectors of immune cell phenotype and function; we also observed significant changes in their corresponding receptor expression [7]. Taken together, these actions result in accelerated inflammation resolution and modulation [8].