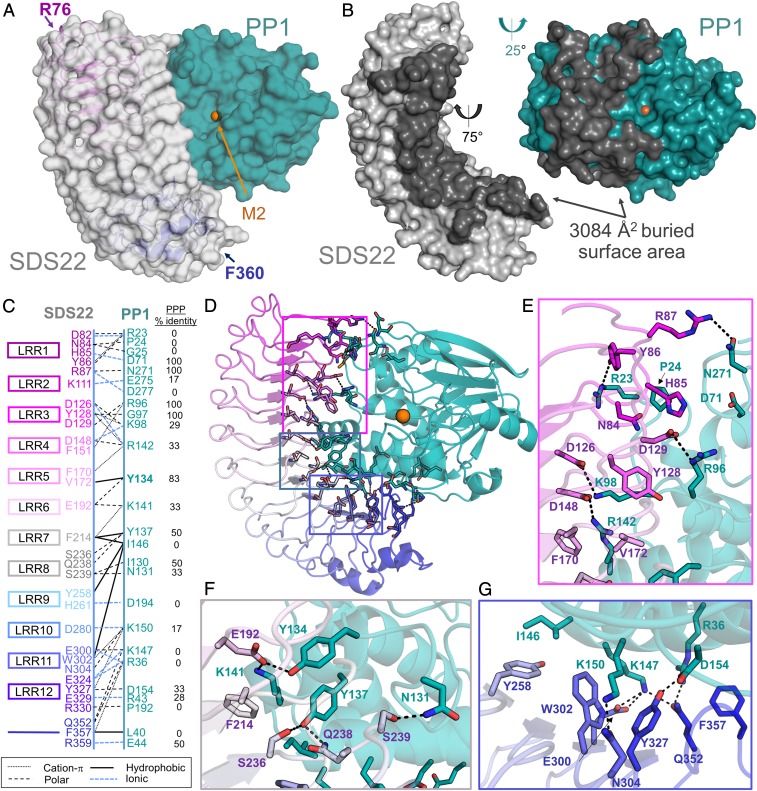
Fig. 2.
SDS22 and PP1 interact via an extensive surface. (A) The SDS22:PP1 complex is shown as a transparent surface (SDS22, gray; PP1, teal). The LRR repeats of SDS22 are colored from magenta (LRR1) to blue (LRR12) and shown as a cartoon with the first and last SDS22 residues indicated. The bound M2 metal (orange sphere) is the location of the PP1 catalytic site. (B) SDS22 (gray) and PP1 (teal) from the SDS22:PP1 complex separated and rotated as indicated to illustrate the binding interface between the 2 proteins (dark gray). (C) Schematic of SDS22 (Left) and PP1 (Right) residues that form polar, ionic, hydrophobic, or cation-π interactions. SDS22 residue names are colored according to the LRR repeat they are a part of. (D) SDS22:PP1 complex shown as a cartoon and colored as in A. The residues that comprise the interface are shown as sticks. Colored boxed areas correspond to the region highlighted in E (magenta), F (gray) and G (blue). (E) Residues that define the SDS22:PP1 interface, focused on LRRs 1–5; polar/ionic interactions are indicated by dashed black lines. (F) The same as E but focusing on the interactions with LRRs 6–8. (G) The same as E but focusing on the interactions with LRRs 9–12.