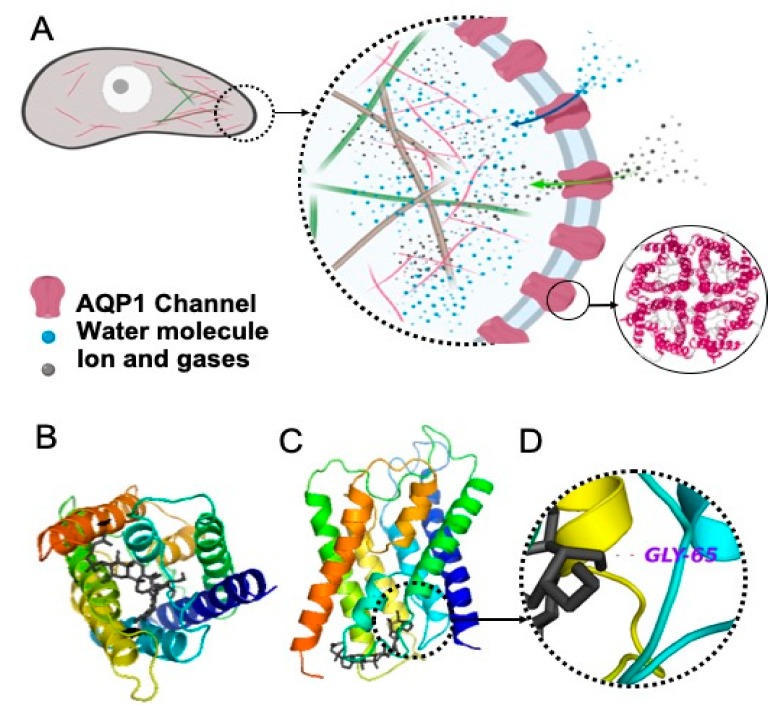
Figure 1.
(A) The role of aquaporin 1 (AQP1) in cell migration and invasion (as reviewed in [39]). AQPs are redistributed to the leading edge of the migrating cell, leading water, ions and gases inside the cell; hence, along with changes in actin polymerisation, they play a role in the forward movement of the cell. AQP1 is a tetramer. Water passes through the pore of each monomer, and ions and gases pass through the central pore of the tetramer. (B) Top view of an AQP1 monomer, being blocked with Rg3, the black structure, (C) Side view of an AQP1 monomer, blocked with Rg3, and (D) H-bonding between Rg3 and Gly 65.