Fig. 1.
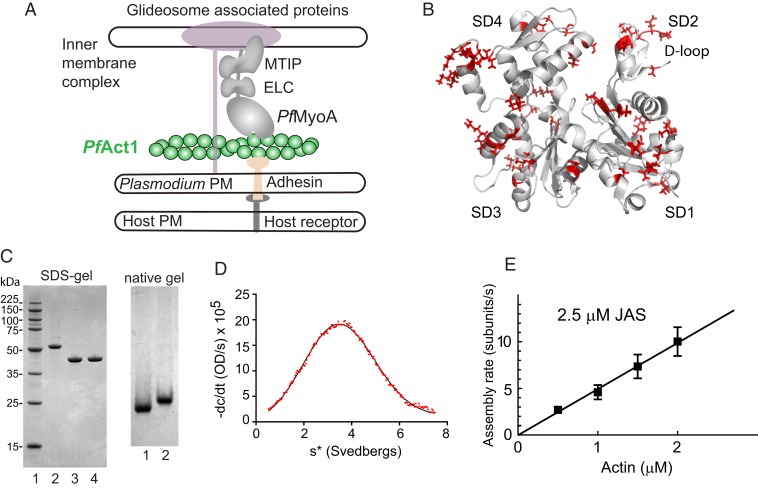
Schematic of PfAct1 in the glideosome, the crystal structure of PfAct1, characterization of expressed PfAct1, and polymerization in the presence of JAS. (A) Schematic of a model of the Plasmodium spp. glideosome (2), the macromolecular complex responsible for gliding motility. The core consists of PfMyoA, a single-headed class XIV myosin with 2 light chains (ELC and MTIP), and a divergent actin, PfAct1. The N terminus of MTIP anchors the myosin motor to the inner membrane complex via glideosome-associated proteins. PfAct1 filaments are anchored to the Plasmodium plasma membrane (PM) via adhesins that bind host receptors from the host plasma membrane. (B) Cartoon of PfAct1 crystal structure (PDB ID code 4CBU), with the 65 residues differing from those found in human β-cytoplasmic actin illustrated with red side chains. The location of the D-loop in subdomain 2 is indicated. SD, subdomain. (C, Left) SDS-gel of (lane 1) molecular mass markers; (lane 2) PfAct1-thymosin following HIS-column; (lane 3) PfAct1-thymosin following chymotryptic cleavage; (lane 4) purified PfAct1 after ion-exchange chromatography. (Right) Native gels of (lane 1), purified PfAct1; (lane 2) skeletal muscle actin. (D) Homogeneity of purified PfAct1 demonstrated by analytical ultracentrifugation. PfAct1 sedimented at 3.2 ± 0.01S (0.2 M ammonium acetate, 5 mM Tris, 0.2 mM Na2ATP, 0.2 mM CaCl2, 0.5 mM DTT, pH 7.5, 20 °C, 0.9 mg/mL PfAct1). s*, sedimentation coefficient. (E) Polymerization rate as a function of actin concentration in the presence of 2.5 µM JAS. See Movie S1 and Table 1 for polymerization rate constants.