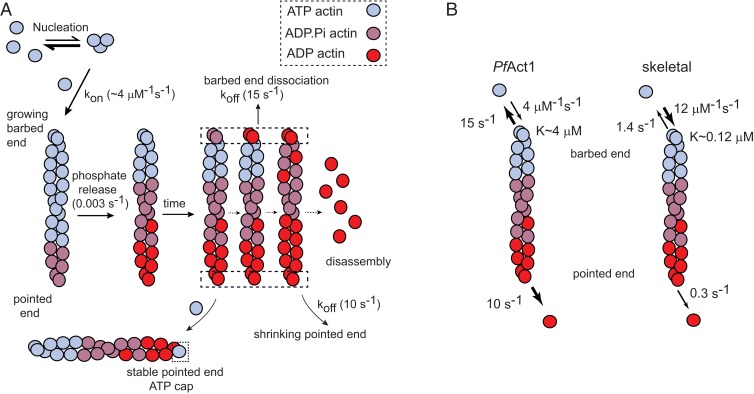
Fig. 5.
Schematic of PfAct1 filament dynamics. (A) Like canonical actins, PfAct1 follows a nucleation–elongation mechanism, but has a very high critical concentration (∼4 µM) due to both a lower assembly rate and a faster disassembly rate than canonical actins. The rates of protomer disassembly from both the barbed and pointed ends are fast (10 to 15 s−1). Treadmilling can be observed near the critical concentration when the rate of elongation becomes similar to the pointed-end disassembly rate. In the absence of added inorganic phosphate or BeFx, the filament composed of ADP protomers completely depolymerizes at long times. Inorganic phosphate, or to a greater extent BeFx, suppresses pointed end dynamics by capping the pointed end with an ATP-like protomers. (B) A comparison of the kinetics of PfAct1 versus skeletal actin filaments. Skeletal rates were taken from ref. 37. Compared with skeletal actin filaments, PfAct1 filaments have a higher critical concentration, a slower assembly rate at the growing barbed end, and faster disassembly kinetics at both ends. The off rates at the barbed and pointed ends are more similar for PfAct1 than for skeletal actin.