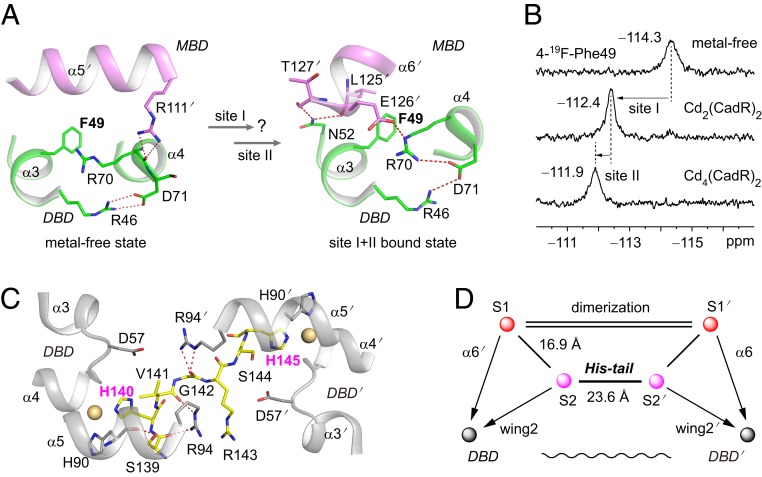
Fig. 2.
Site I and site II are both allosteric sites. (A) The phenylalanine biomarker, Phe49, located at the interface between the DBD and MBD for probing the allosteric motion triggered by cadmium binding in site I and site II. Hydrogen bonds are represented by red dashed lines. (B) NMR spectra of the 19F-labeled protein titrated by cadmium ion. (C) Close up view of the interaction network around the His-tail region. The cadmium ions in sites S2 and S2′ are shown as spheres. The His-tail region (residues 139 to 145, SHVGRSH) is shown as yellow sticks. (D) Schematic model representing the topological arrangement of metal-binding sites and the DBD. The metal-binding sites are connected by the dimerization helices and the His-tail. The dimerization helices (α5 and α5′) are represented by double lines. The allosteric regulation pathways are indicated by arrows. The long-range communication of 2 DBDs through the His-tail is indicated as a wavy line.