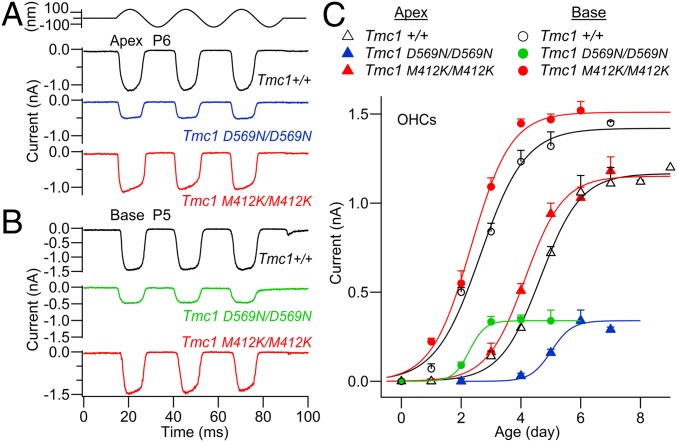
Fig. 2.
MET currents in OHCs of Tmc1 D569N; Tmc2−/− and Tmc1 M412K; Tmc2−/− mice. (A) Examples of maximal MET currents in apical OHCs of Tmc1+/+, Tmc1 D569N/D569N, and Tmc1 M412K/M412K at P6. (B) Maximal MET currents in basal OHCs of Tmc1+/+ and Tmc1 D569N/D569N and Tmc1 M412K/M412K at P5. At both cochlear locations, the maximal MET current is smaller in D569N. (C) Development of MET current (mean ± SEM) with postnatal age. Number of OHCs with points of increasing age—Tmc1+/+Tmc2−/−: base, open circles, 4, 5, 5, 4, 4, 3; Tmc1+/+Tmc2−/−: apex, open triangles, 3, 3, 3, 5, 7, 5, 6, 3; Tmc1 M412K/M412K; Tmc2−/−: base, red circles, 3, 3, 4, 4, 5, 2; Tmc1 M412K/M412K; Tmc2−/−: apex, red triangles, 2, 5, 11, 9, 10, 6; Tmc1 D569N/D569N; Tmc2−/−: base, green circles, 2, 4, 5, 7, 4; and Tmc1 D569N/D569N; Tmc2−/−: apex, blue triangles, 3, 3, 6, 9, 5.