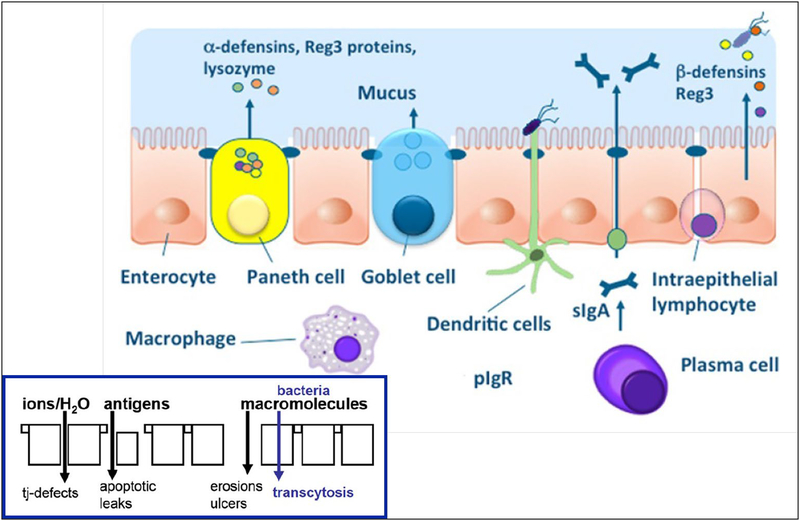
Figure 2.
Intestinal barrier and its dysfunctions. The intestinal barrier includes the mucus layer preventing bacterial adhesion by secretion of chemicals such as α-defensins and IgA secretion, epithelial cells, connected at the tight junctions (tj) by junctional complexes, having the ability to transport luminal content and react to noxious stimuli by secretion of chloride and antimicrobial peptides, and the lamina propria innate and acquired immunity cells secreting Ig and cytokines. Intestinal permeability measurements are determined by the marker molecules used for measurement, since the type of molecules that pass the intestinal barrier depends on the type of lesion. Reproduced from ref. 18.