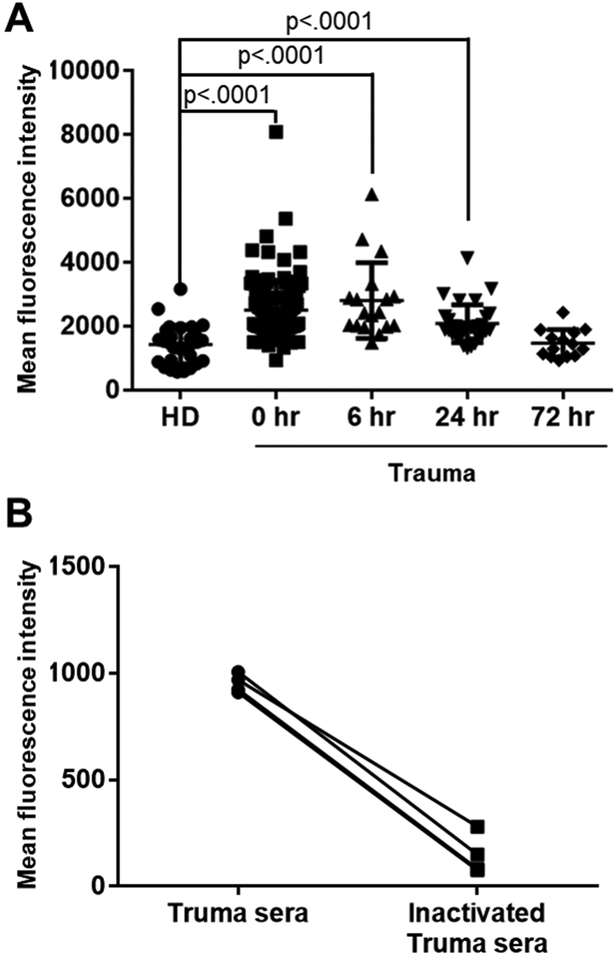
Figure 6. Nitric oxide (NO) production by RBCs induced by trauma serum.
NO production from healthy RBCs (type O, Rh negative) measured by flow cytometry after incubation with sera from trauma patients or healthy donors by using DAF-FM diacetate. NO production from RBCs was expressed as mean fluorescence intensity of DAF-FM diacetate fluorescence. A, we used 104 samples from trauma patients (n, 0 hour =104, 6 hour =18, 24 hour =31 and 72 hour =14) and 38 samples from healthy donors (HD). The mean fluorescence intensity [Mean ± SD (min - max)] of nitric oxide production was [1568 ± 730 (578 – 3455)] for healthy donors, [2542 ± 934 (1392– 8093)] for 0 hour, [2809 ± 1189 (1488 – 6137)] for 6 hour, [2084 ± 594 (1318–4134)] for 24 hour and [1469 ± 430 (935 – 2437)] for 72 hour patients. B, Heat inactivation of complement in sera from trauma patients eliminates their ability to trigger NO production. To inactivate complement, sera were incubated 55°C for 30 min. RBCs were incubated with sera from trauma patients before or after inactivation of complement. Individual sera with/without inactivation of complement are shown. Straight lines are used to connect individual points to help visualize how different they are in each sample.