Figure 1.
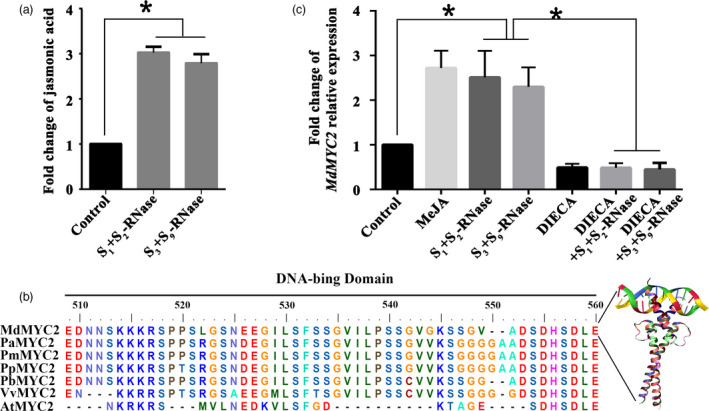
S‐RNase induces the JA‐MdMYC2 signalling pathway in pollen tubes. (a) Pollen tubes from ‘Ralls Janet’ were treated with 30 μg/mL of S 1 +S 2 ‐RNase and S 3 +S 9 ‐RNase, respectively, and then collected the pollen tubes. Fold change of jasmonic acid content in ‘Ralls Janet’ pollen tubes treated with 30 μg/mL of S 1 +S 2 ‐RNase and S 3 +S 9 ‐RNase. Control, untreated pollen tubes. (b) Comparison of the deduced amino acid sequence of MdMYC2 with MYC2 protein sequences from other plant species. The DNA‐binding domain is shown as a black bar above the alignment. AtMYC2 is from Arabidopsis thaliana, PaMYC2 is from Prunus avium, PmMYC2 is from Prunus mume, PpMYC2 is from Prunus persica, PbMYC2 is from Pyrus bretschneideri, and VvMYC2 is from Vitis vinfera. (c) Fold change of MdMYC2 relative expression. qRT‐PCR analysis of MdMYC2 expression in pollen tubes following various treatments. Pollen tubes were treated with 30 μg/mL of S 1 +S 2 ‐RNase and S 3 +S 9 ‐RNase, 30 μm methyl jasmonate 30 μm (MeJA), sodium diethyldithiocarbamate (DIECA) and 30 μg/mL of S 1 +S 2 ‐RNase and S 3 +S 9 ‐RNase after DIECA treatment. Control, untreated pollen tubes. The final data were normalized to the expression in the untreated pollen tubes (control). Values are means + SD of three biological replicates. Asterisks indicate significantly different values (*P < 0.05).
