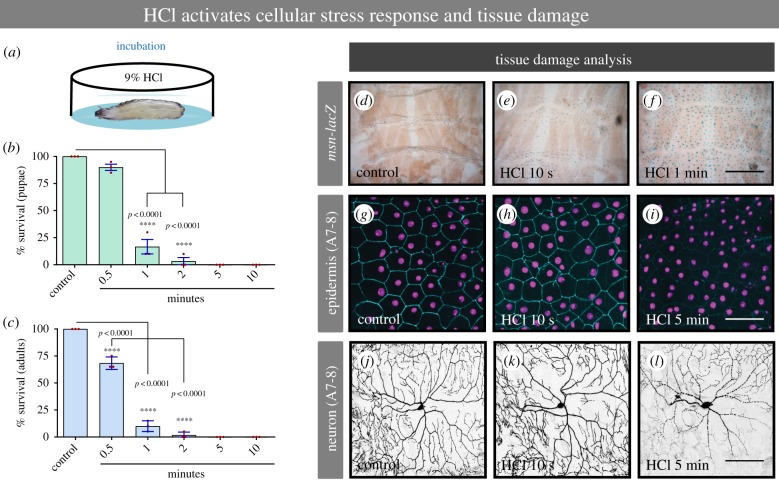
Figure 2.
Noxious chemical stimulus induces cellular stress response and tissue damage. (a) Cartoon depicting the larvae incubation in 9% HCl. (b,c) Larval and adult survival per cent in response to increasing time of incubation with 9% HCl. (d–f) Epidermal cell stress response induced by 9% HCl. (g–i) Epidermal tissue damage analysis in response to noxious acid. (j–l) Class IV sensory neuronal tissue damage in response to noxious acid. A7-8: Abdominal segments 7 or 8. msn-lacZ: reporter of Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) signalling/cellular stress. (b,c) n = 60 for each condition. Error bars represent mean ± s.e. Statistical significance was determined via one-way ANOVA with a Dunnet's post hoc test. (d–f) n = 4 larvae for each condition; (g–l) n = 9 larvae for each condition and representative images are shown. Bar in d–f, 50 µm. Bar in g–l, 100 µm.