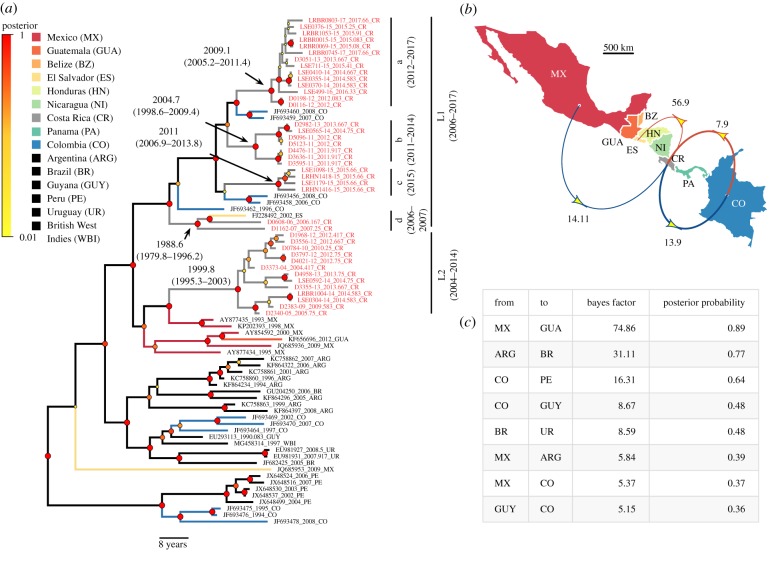
Figure 1.
Bayesian phylogenetic inference of international dispersal histories of vampire bat rabies. (a) Phylogenetic tree with branches coloured by the country of origin. Black branches signal countries omitted from the map in (b). Node circle size and colours indicate posterior probabilities on branch partitions. Red tip labels indicate viruses from Costa Rica. (b) Summary of statistically supported (BF > 5) viral dispersions between countries, restricted to those involving Costa Rica. Arrow colours represent northbound (red) or southbound (blue) dispersals, with width proportional to the number of Markov jumps (range = 0.9–2.2). Arrows are annotated with the BF support for dispersals between countries. (c) Additional transitions supported in the discrete phylogeographic analysis that did not involve Costa Rica occurred predominately between geographical neighbours. Country name abbreviations in (b) and (c) match (a). (Online version in colour.)