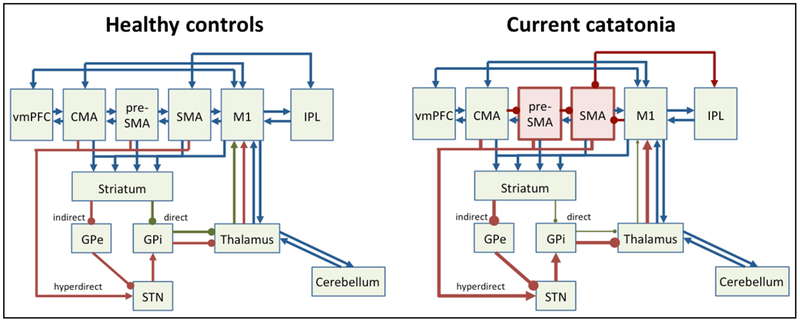
Figure 1. Motor network pathology in catatonia.
Left panel depicts motor system in healthy controls, right panel in current hypokinetic catatonia. Cortical (pre)motor areas are: ventromedial prefrontal cortex (vmPFC), cingulate motor area (CMA), pre-supplementary motor area (pre-SMA), supplementary motor area (SMA), primary motor cortex (M1), and inferior parietal lobe (IPL). GPe = external globus pallidus, GPi = internal globus pallidus, STN = subthalamic nucleus. Green arrows indicate net facilitatory pathways, such as the direct pathway. Red arrows indicate net inhibitory pathways, such as indirect or hyperdirect pathways. Blue arrows indicate neutral or modulatory connections.
Note: in catatonia preSMA and SMA have increased neural activity concurrently with motor behavioral inhibition, which may either result from cortico-cortical inhibition or from dominant indirect/hyperdirect pathway activity.