Figure 1.
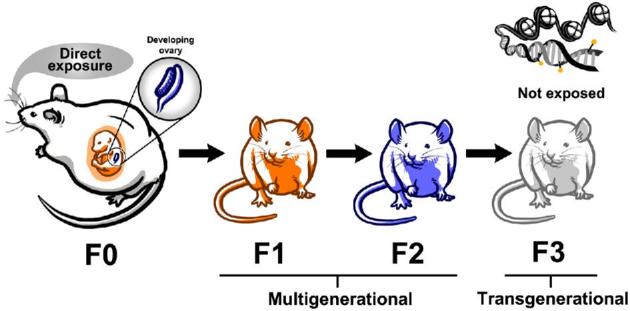
Exposure to endocrine disruptors during prenatal development causes multigenerational effects in the F1 and F2 generations and transgenerational effects in the F3 generation. The F1 and F2 generations are directly exposed to the endocrine disruptor as a fetus and germ cell, respectfully. The F3 generation is not directly exposed and the mechanisms governing the effects in the F3 generation are thought to be epigenetic in nature.
