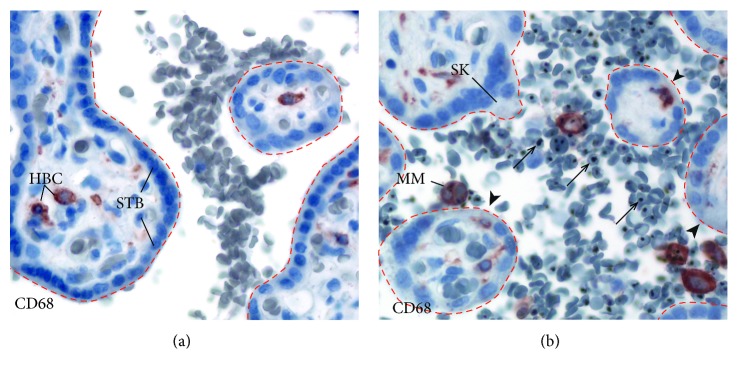
Figure 1.
(a) Normal placenta. The dashed lines outline placental villi. Maternal RBCs are seen in the intervillous space. The placental villous (outlined with red dotted lines) is lined by the syncytiotrophoblast (STB). Fetal Hofbauer cells (HBCs) are located in the villous core. (b) Malaria-infected placenta. iRBCs (arrows) accumulate in the intervillous space, and the villous surface is denuded (arrowhead). Infected red blood cells (arrows) and maternal intervillous monocytes (MIM) are found within the intervillous space. A syncytial knot (SK) is a histologic sign of placental remodeling from pathologic processes. HBC: Hofbauer cell; STB: syncytiotrophoblast; MIM: maternal intervillous monocyte; SK: syncytial knot. Placental biopsies were stained with CD68, a monocyte/macrophage marker, and counterstained with hematoxylin.