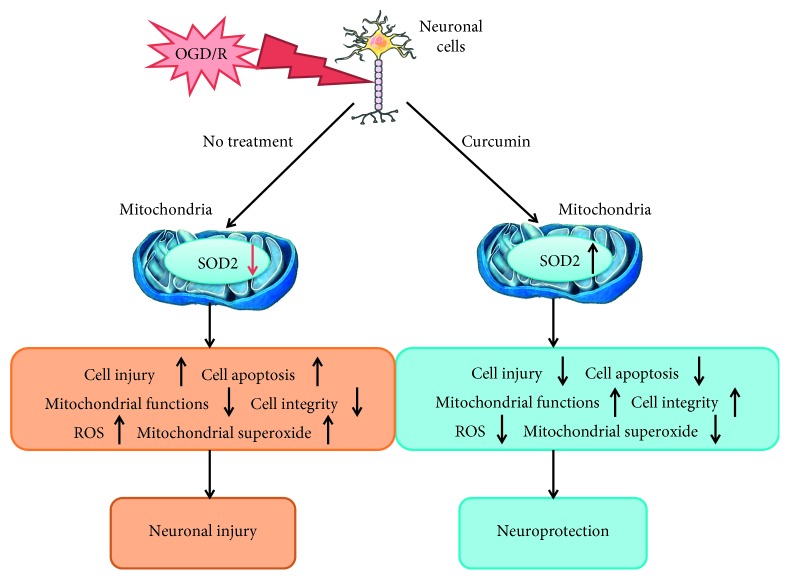
Figure 7.
Curcumin induces neuroprotection against OGD/R in neuronal cells via upregulating SOD2 protein. Oxygen-glucose deprivation and reoxygenation (OGD/R) injury can downregulate SOD2 expression, increase intracellular ROS and mitochondrial superoxide accumulations, then damage neuronal cells, increase cell apoptosis, cause mitochondrial dysfunctions, and undermine cell integrity, leading to neuronal injury ultimately. Coadministration of curcumin, however, could upregulate SOD2 expression, reduce intracellular ROS and mitochondrial superoxide accumulations, and ameliorate mitochondrial functions and cell integrity, causing neuroprotection.