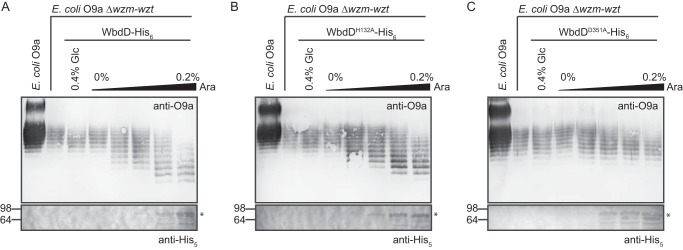
Figure 2.
The kinase domain of WbdD is sufficient for chain termination in vivo. Levels of WbdD-His6 (expressed from pWQ470) (A) and its mutants with inactivated methyltransferase (His132 → Ala; pWQ829) (B) or kinase (Asp351 → Ala; pWQ830) (C) catalytic sites were titrated in E. coli CWG638 manA Δwzm-wzt::aphA-3. The addition of 0.4% d-glucose was used to repress the pBAD promoter, whereas varying concentrations of l-arabinose induced expression of the WbdD variants. To overcome second site mutations occurring during prolonged growth in the absence of functional O-PS export (17), a manA mutant was used, making O9a O-PS biosynthesis conditional on the addition of mannose to the growth medium at the beginning of the experiment. Und-PP–linked O-PS intermediates (accumulating in the absence of transport) were detected in proteinase K–digested whole-cell lysates by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting with O9a-specific antibodies (top panels). The control lane is authentic O9a LPS from the manA strain (CWG634). The bottom panels show the detection of WbdD-His6 variants by immunoblotting with anti-His5 antibodies.