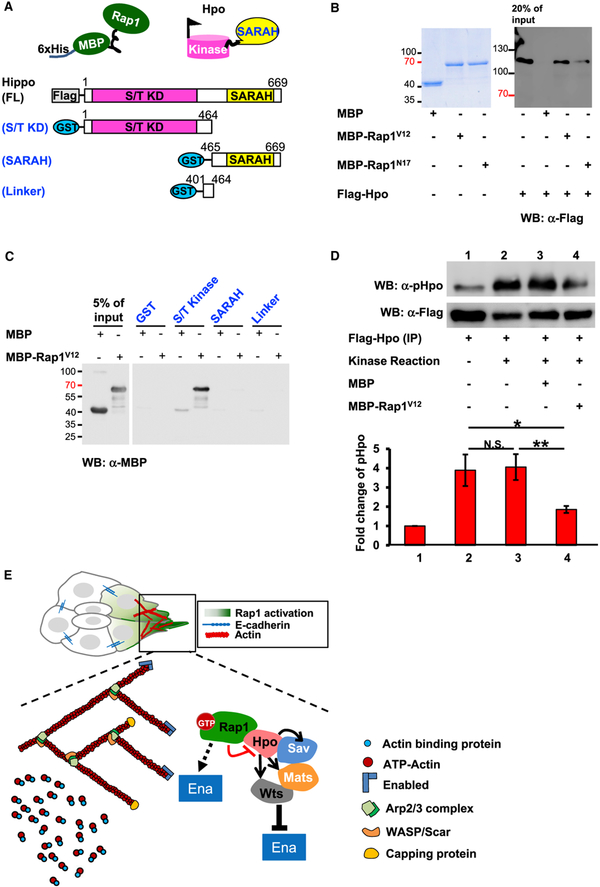
Figure 7. Rap1 Interacts with Hpo to Suppress Its Kinase Activity.
(A) A schematic diagram of full-length Hpo and its deletion constructs used in this study.
(B) SDS-PAGE gel stained with Coomassie blue showing the bacterially expressed MBP fusion proteins. Rap1 recombinant proteins are incubated in cell lysate containing FLAG-Hpo, and the precipitated complexes were subjected to western blotting (WB) with anti-FLAG antibody.
(C) WB with anti-MBP antibody revealing which of the Hpo domains pulls down MBP-Rap1V12.
(D) Hpo autophosphorylation is analyzed by immunoblot with anti-Hpo-pThr195 antibody, and the optical density ratio is normalized with FLAG-Hpo protein (α-FLAG). *p < 0.5, **p < 0.01. N.S. means not significant.
(E) Model of the Rap1-Hpo pathway in BC polarization. At the front of migratory clusters, GTP-bound Rap1 binds to Hpo to prevent its activation, relieving Ena/VASP suppression and promoting actin polymerization to advance BC migration. The error bars represent SD.