Figure 5. HDAC inhibition synergizes with Hsp90 inhibition to induce apoptosis in bladder cancer.
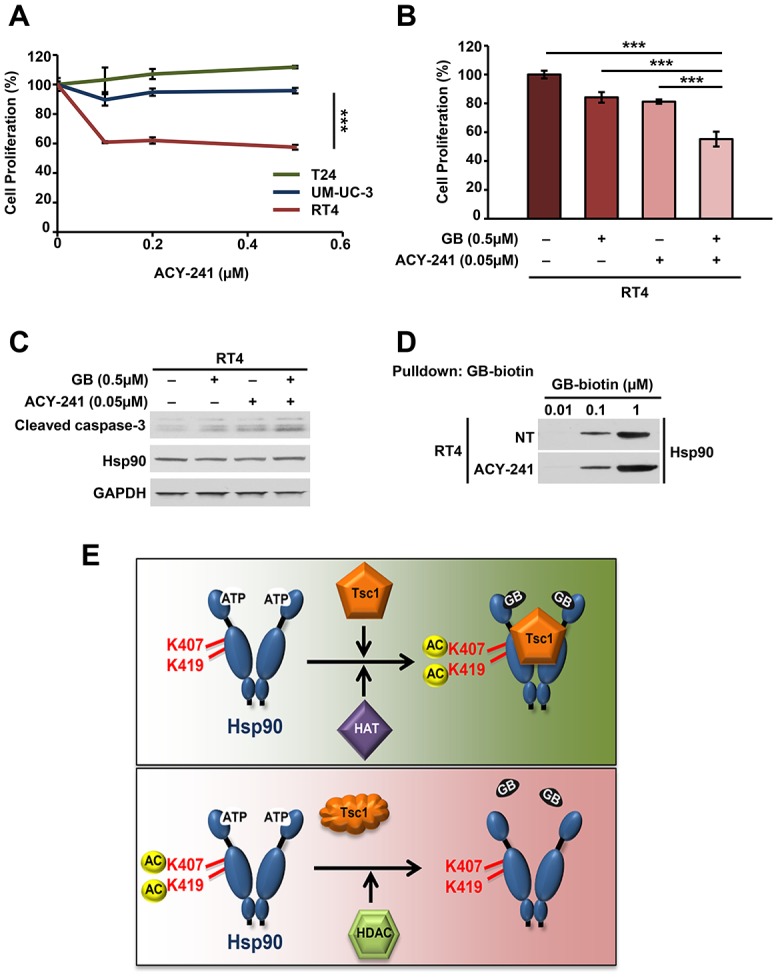
(A) Sensitivity of T24, UM-UC-3 and RT4 cells to increasing concentrations of ACY-241 was determined by WST proliferation assay. A Student’s t-test was performed to assess statistical significance (*** p < 0.001). (B) RT4 cells were treated with or without 0.5μM ACY-241 for 16 hr followed by 0.5μM ganetespib for an additional 48 hr. Cell viability was then determined by WST proliferation assay. A Student’s t-test was performed to assess statistical significance (*** p < 0.001). (C) Immunoblot of apoptotic marker cleaved caspase-3 in RT4 cells from (B). (D) Hsp90 binding to biotinylated-ganetespib was examined in RT4 cells treated with or without 1 μM ACY-241 for 16 hr. (E) Impact of the co-chaperone Tsc1 on Hsp90 binding to its inhibitors. Tsc1 facilitates acetylation of Hsp90-K407/K419. In the absence of Tsc1, Hsp90 is hypoacetylated at these residues and binds less avidly to its inhibitors. HDAC inhibitor treatment restores Hsp90 acetylation and bladder cancer cell sensitivity to Hsp90 inhibitors.
