Figure 1.
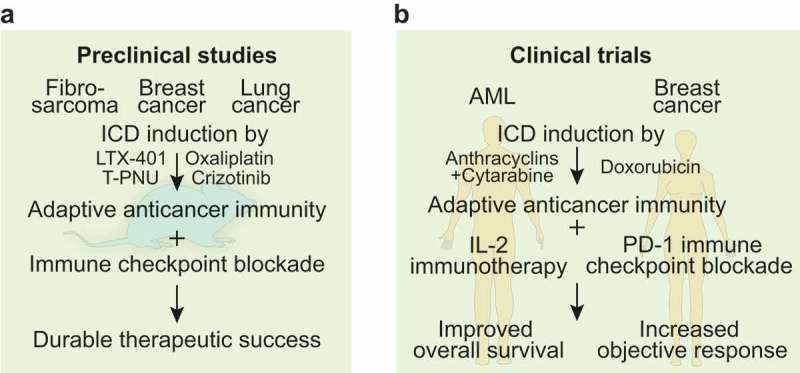
Preclinical and clinical evidence for immunogenic cell death-mediated sensitization to immune checkpoint blockade.
(A). Preclinical work in syngeneic mouse models of fibrosarcoma, breast and lung cancer depicted the potency of immunogenic cell death (ICD) induced by agents such as the oncolytic compound LTX-401, the antibody drug conjugate T-PNU, the tyrosine kinase inhibitor crizotinib and the chemotherapeutic agent oxaliplatin to trigger adaptive anticancer immunity. Sequential combination with immune checkpoint blockade achieved durable therapeutic success. (B). Clinical trials in patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) that received consolidation therapy with anthracyclins and cytarabine followed by interleukin-2 (IL-2)-based immunotherapy or women with triple negative breast cancer that received doxorubicin before immune checkpoint inhibition with monoclonal anti-PD-1 antibodies depicted improved overall survival and increased objective response, respectively.
