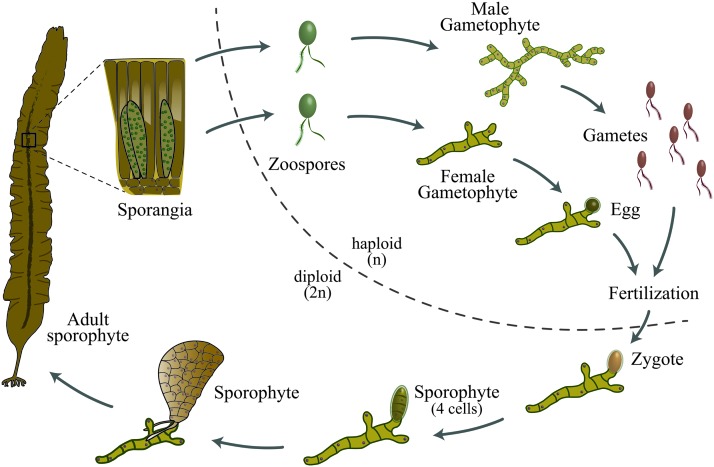
FIG. 1.
Life cycle of kelp (e.g., Saccharina latissima). During meiosis, zoospores (n) are formed in sporangia by a large multicellular sporophyte (2n). The spores settle onto the seafloor and develop into male and female gametophytes (n). Sterile gametophytes can be clonally propagated, and used as seed stock for further breeding and cultivation. Male and female gametophyte form antheridia that produce sperm and oogonia that produce eggs, respectively. The sperm fertilizes the egg, and a zygote is formed that develops into a sporophyte (2n). Color images are available online.