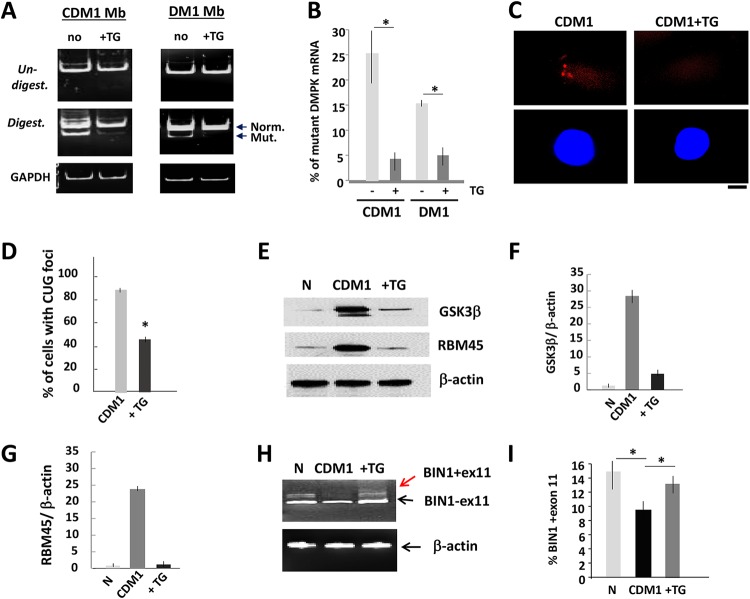
FIG 1.
Reduction of the mutant DMPK mRNA and correction of CUGBP1 and MBNL1 activities in DM1 myoblasts treated with TG. (A) Mutant DMPK mRNA is reduced in CDM1 and DM1 myoblasts (Mb) treated with TG. DMPK levels were analyzed by qRT-PCR, and the same amounts of PCR products were digested with Bpm1. Normal and mutant DMPK products are shown by arrows. GAPDH control is shown on the bottom. (B) Quantification of the mutant DMPK shown in panel A. The sum of the signals for normal and mutant DMPK mRNA was set at 100%, and the percentages of the mutant DMPK were determined. (C, top) Representative FISH images of CDM1 myoblasts, treated with vehicle or TG, using CAG probe. (Bottom) Nuclei stained with DAPI. The scale bar is 5 μm. (D) Percentage of CDM1 myoblasts containing CUG foci after treatment with the vehicle or TG. Total number of analyzed cells was set at 100%. (E) GSK3β and a downstream myogenic target of CUGBP1, RBM45, are corrected in CDM1 myoblasts treated with TG. Western blot analysis shows the levels of GSK3β and RBM45 in normal (N) myoblasts and untreated and TG-treated CDM1 myoblasts. β-Actin was a loading control. (F and G) Quantification of GSK3β and RBM45 signals as ratios to β-actin levels shown in panel E. (H) Correction of BIN1 splicing in CDM1 myotubes treated with TG. qRT-PCR of BIN1 in normal and in untreated and TG-treated CDM1 myotubes. β-Actin was used as the control. Arrows show two isoforms with inclusion and exclusion of exon 11. (I) Quantitative analysis of BIN1 isoform, including exon 11, shown in panel H. *, P < 0.05.