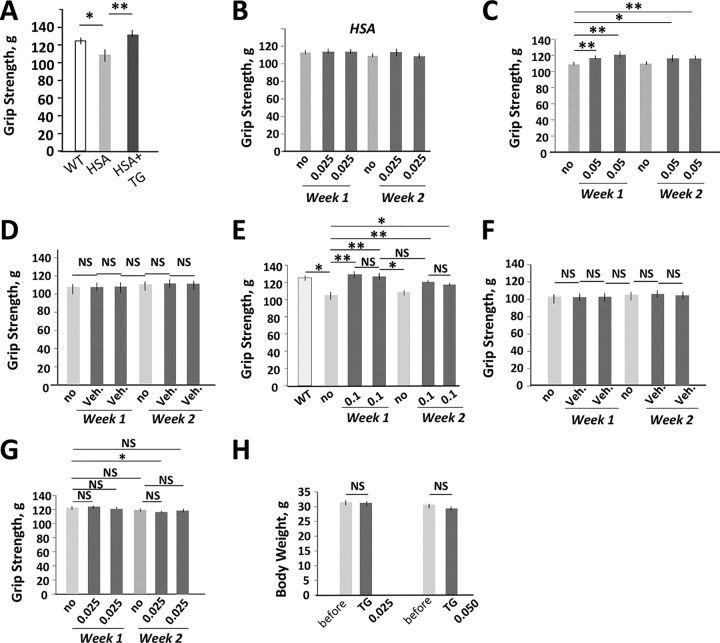
FIG 4.
Reduction of the mutant CUG repeats in the TG-treated HSALR mice is accompanied by a quick positive effect on grip weakness. (A) A single dose of the oral TG (0.1 μg/g) corrects grip weakness in 6-month-old HSALR mice (females) ∼24 h after treatment. The grip strength was measured before the treatment and the day after treatment. The matched WT mice were used as a control. The groups of WT and HSALR mice contained 5 to 6 mice. (B to D) Grip strength analysis of 4-month-old HSALR mice (males) (n = 5) treated with 0.025 μg/g of TG (B), 0.05 μg/g of TG (C), or vehicle (D). (E and F) Grip strength analysis of 6-month-old HSALR mice (females) (n = 6) treated with 0.1 μg/g of TG (E) or vehicle (F). (G) TG has no effect on the grip strength of adult WT mice. A group of WT mice (FVB, males, n = 6) was treated with 0.025 μg/g of TG, and the grip strength was measured according to the protocol shown in Fig. 3A. A minor (but significant) reduction of grip strength in WT mice was observed at one time point of the treatment with TG (0.025 μg/g) relative to untreated mice; however, this effect was not reproduced with a higher dose of TG (0.05 μg/g). This might occur due to a negative effect of the repetitive oral gavage procedure on mouse performance. (H) TG has no significant effect on the body weight of WT mice. WT mice (n = 6) were treated with TG according to the protocol described for Fig. 3A. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01. NS, nonsignificant change.