Figure 2. Cross-Linking Mass Spectrometry of SWI/SNF Complexes Reveals Conserved Connectivity of Interacting Modules.
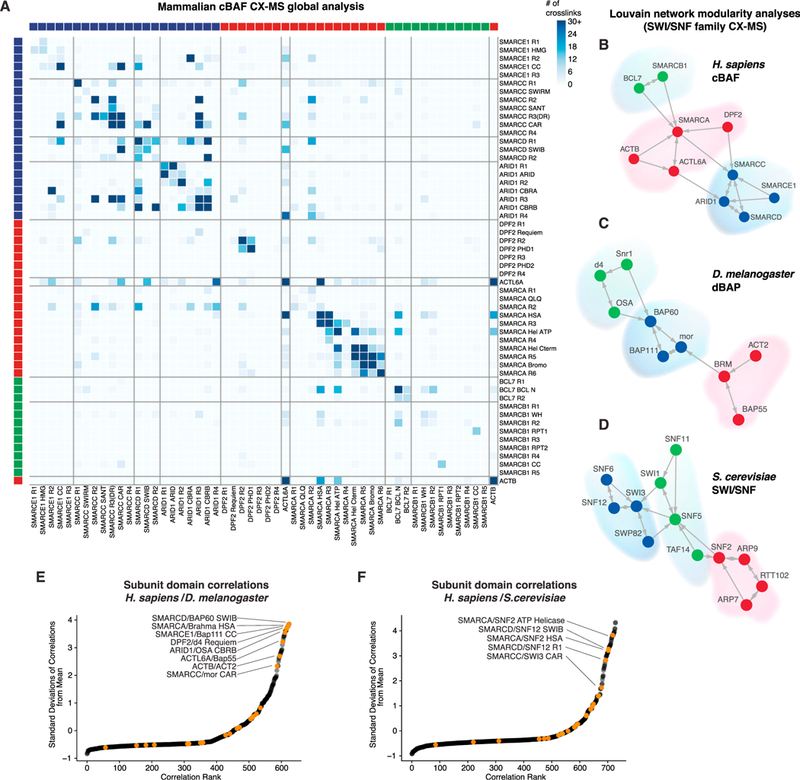
(A) Matrix heatmap of the total crosslinks identified in combined HA-SS18 and HA-DPF2 BAF complex cross-linking mass spectrometry datasets. Individual subunits are divided into domains and ordered according to modules in (B). See also Figures S2B, S2J, and S2K.
(B-D) Louvain modularity analysis performed on (B) mammalian cBAF complex cross-linking mass spectrometry datasets, (C) D. melanogaster D4 and BAP60 cross-linking mass spectrometry datasets, and (D) S. cerevisiae cross-linking mass spectrometry datasets (from Sen et al., 2017).
(E) Correlations between mammalian and Drosophila BAF or BAP subunit domain and region interactions from cross-linking mass spectrometry datasets. See also Figures S2B and S2J.
(F) Correlations between mammalian and yeast SWI/SNF subunit domain and region interactions from cross-linking mass spectrometry datasets. See also Figures S2B and S2K.
See also Figure S2.
